Risk factors associated with post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2: an N3C and NIH RECOVER study
- PMID: 37880596
- PMCID: PMC10601201
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-023-16916-w
Risk factors associated with post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2: an N3C and NIH RECOVER study
Abstract
Background: More than one-third of individuals experience post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC, which includes long-COVID). The objective is to identify risk factors associated with PASC/long-COVID diagnosis.
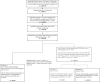
Methods: This was a retrospective case-control study including 31 health systems in the United States from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C). 8,325 individuals with PASC (defined by the presence of the International Classification of Diseases, version 10 code U09.9 or a long-COVID clinic visit) matched to 41,625 controls within the same health system and COVID index date within ± 45 days of the corresponding case's earliest COVID index date. Measurements of risk factors included demographics, comorbidities, treatment and acute characteristics related to COVID-19. Multivariable logistic regression, random forest, and XGBoost were used to determine the associations between risk factors and PASC.
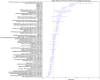
Results: Among 8,325 individuals with PASC, the majority were > 50 years of age (56.6%), female (62.8%), and non-Hispanic White (68.6%). In logistic regression, middle-age categories (40 to 69 years; OR ranging from 2.32 to 2.58), female sex (OR 1.4, 95% CI 1.33-1.48), hospitalization associated with COVID-19 (OR 3.8, 95% CI 3.05-4.73), long (8-30 days, OR 1.69, 95% CI 1.31-2.17) or extended hospital stay (30 + days, OR 3.38, 95% CI 2.45-4.67), receipt of mechanical ventilation (OR 1.44, 95% CI 1.18-1.74), and several comorbidities including depression (OR 1.50, 95% CI 1.40-1.60), chronic lung disease (OR 1.63, 95% CI 1.53-1.74), and obesity (OR 1.23, 95% CI 1.16-1.3) were associated with increased likelihood of PASC diagnosis or care at a long-COVID clinic. Characteristics associated with a lower likelihood of PASC diagnosis or care at a long-COVID clinic included younger age (18 to 29 years), male sex, non-Hispanic Black race, and comorbidities such as substance abuse, cardiomyopathy, psychosis, and dementia. More doctors per capita in the county of residence was associated with an increased likelihood of PASC diagnosis or care at a long-COVID clinic. Our findings were consistent in sensitivity analyses using a variety of analytic techniques and approaches to select controls.
Conclusions: This national study identified important risk factors for PASC diagnosis such as middle age, severe COVID-19 disease, and specific comorbidities. Further clinical and epidemiological research is needed to better understand underlying mechanisms and the potential role of vaccines and therapeutics in altering PASC course.
Keywords: COVID-19; Long-COVID; PASC; Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2; Risk factors.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to report. NIH grants received to conduct this research are listed below.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. COVID 19 Special Issue. 2020;10. 10.46945/bpj.10.1.03.01
-
- CDC. Estimated COVID-19 burden. In: Centers for disease control and prevention [Internet]. 4 Mar 2022 [cited 27 May 2022]. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/burden.html
-
- Clinical Services, Systems. A clinical case definition of post COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. World Health Organization; 6 Oct 2021 [cited 11 May 2022]. Available: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Post_COVID-19_cond...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UM1 TR004404/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002649/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001860/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104942/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003096/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004556/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104938/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002537/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001412/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001872/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001878/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002529/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002494/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002736/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002369/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002541/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115371/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES001247/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002001/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002538/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004406/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115458/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002535/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003167/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 HL161847/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001409/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001449/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001453/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002489/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104940/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003107/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003015/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002733/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG070329/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 TR002306/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001876/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001436/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002384/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002553/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002389/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001414/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104941/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002014/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002550/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002319/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001855/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002373/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002240/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K01AG070329/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002556/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003017/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001998/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002645/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002366/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115428/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002377/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115677/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002544/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003098/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous