An Overview on Electrophysiological and Neuroimaging Findings in Dyslexia
- PMID: 37881421
- PMCID: PMC10593994
- DOI: 10.18502/ijps.v18i4.13638
An Overview on Electrophysiological and Neuroimaging Findings in Dyslexia
Abstract
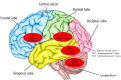
Objective: Dyslexia is a prevalent neurodevelopmental condition that is characterized by inaccurate and slow word recognition. This article reviews neural correlates of dyslexia from both electrophysiological and neuroimaging studies. Method : In this brief review, we provide electrophysiological and neuroimaging evidence from electroencephalogram (EEG) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies in dyslexia to understand functional and structural brain changes in this condition. Results: In both electrophysiological and neuroimaging studies, the most frequently reported functional impairments in dyslexia include aberrant activation of the left hemisphere occipito-temporal cortex (OTC), temporo-parietal cortex (TPC), inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), and cerebellar areas. EEG studies have mostly highlighted the important role of lower frequency bands in dyslexia, especially theta waves. Furthermore, neuroimaging studies have suggested that dyslexia is related to functional and structural impairments in the left hemisphere regions associated with reading and language, including reduced grey matter volume in the left TPC, decreased white matter connectivity between reading networks, and hypo-activation of the left OTC and TPC. In addition, neural evidence from pre-reading children and infants at risk for dyslexia show that there are abnormalities in the dyslexic brain before learning to read begins. Conclusion: Advances in comprehending the neural correlates of dyslexia could bring closer translation from basic to clinical neuroscience and effective rehabilitation for individuals who struggle to read. However, neuroscience still has great potential for clinical translation that requires further research.
Keywords: Brain Waves; Dyslexia; Electroencephalogram (EEG); Neuroimaging; Neuropathology.
Copyright © 2023 Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dyslexic children lack word selectivity gradients in occipito-temporal and inferior frontal cortex.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Feb 26;7:742-54. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.02.013. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 25844326 Free PMC article.
-
Neural deficits in children with dyslexia ameliorated by behavioral remediation: evidence from functional MRI.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Mar 4;100(5):2860-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0030098100. Epub 2003 Feb 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12604786 Free PMC article.
-
The Functional Neuroanatomy of Developmental Dyslexia Across Languages and Writing Systems.Front Psychol. 2020 Feb 5;11:155. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00155. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32116951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-world EEG network analysis of functional connectivity in developmental dyslexia after visual training intervention.J Integr Neurosci. 2020 Dec 30;19(4):601-618. doi: 10.31083/j.jin.2020.04.193. J Integr Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33378835
-
Comparative research on neural dysfunction in children with dyslexia under different writing systems: A meta-analysis study.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jun;137:104650. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104650. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 35367220 Review.
Cited by
-
On the Effects of Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation Techniques on Developmental Dyslexia: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Iran J Psychiatry. 2025 Apr;20(2):209-222. doi: 10.18502/ijps.v20i2.18203. Iran J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40521277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overt Word Reading and Visual Object Naming in Adults with Dyslexia: Electroencephalography Study in Transparent Orthography.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 May 4;11(5):459. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11050459. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Surushkina SY, Yakovenko E, Chutko L, Didur M. Dyslexia as a multifactorial disorder. Neurosci Behav. 2021;51:303–8.
-
- Boyes ME, Leitão S, Claessen M, Badcock NA, Nayton M. Correlates of externalising and internalising problems in children with dyslexia: An analysis of data from clinical casefiles. Aust Psychol. 2020;55(1):62–72.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources