Dual-emissive solid-state histidine-stabilized gold nanoclusters for applications in white-light generation
- PMID: 37881697
- PMCID: PMC10597560
- DOI: 10.1039/d3na00555k
Dual-emissive solid-state histidine-stabilized gold nanoclusters for applications in white-light generation
Abstract
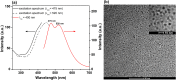
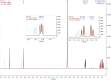
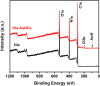
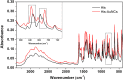
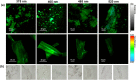
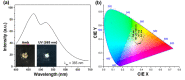
The majority of present-day white-light emitting devices (WLEDs) are built upon the use of rare-earth elements, which have a short supply, are expensive and can become extremely toxic. Thus, in this work, we synthesized an eco-friendly, efficient and cheap white-light emitting material (WLEM) based on solid-state histidine-stabilized gold nanoclusters (His-AuNCs), obtained through the lyophilization of microwave-synthesized photoluminescent His-AuNCs. Their morphological and structural characterization was followed by thorough evaluation of their intrinsic solid-state photoluminescence properties via steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy and microscopy, at multiple excitation wavelengths. A white-light emission was observed under UV light excitation due to the two-band broad emission, with maxima at 475 and 520 nm, covering a large area of the visible spectrum. In order to evaluate the purity of the white-light emission we calculated the chromaticity coordinates, at different wavelengths, and displayed them on a CIE (Commision Internationale d'Eclairage) diagram. An excellent value of (0.36, 0.33) was found at 420 nm excitation, which falls within the range of pure white-light emission. Moreover, the His-AuNCs show great photo- and thermo-stability, thus proving their ability to perform as a reliable WLEM with potential use in the development of eco-friendly WLEDs.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

