How we manage a high D-dimer
- PMID: 37881856
- PMCID: PMC10985443
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2023.283966
How we manage a high D-dimer
Abstract
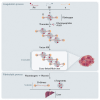
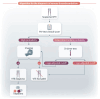
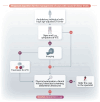
D-dimer, a soluble fibrin degradation product that originates from plasmin-induced degradation of cross-linked fibrin, is an important biomarker of coagulation activation and secondary fibrinolysis that is routinely used to rule out venous thromboembolism (VTE), and to evaluate the risk of VTE recurrence, as well as the optimal duration of anticoagulant therapy. Besides VTE, D-dimer may be high due to physiologic conditions, including aging, pregnancy, and strenuous physical activity. In addition, several disorders have been associated with increased D-dimer levels, ranging from disseminated intravascular coagulation to infectious diseases and cancers. Thus, it is far from unusual for hematologists to have to deal with ambulatory individuals with increased D-dimer without signs or symptoms of thrombus formation. This narrative review is dedicated to the management of these cases by the hematologist.
Figures
References
-
- Lippi G, Favaloro EJ. Laboratory hemostasis: from biology to the bench. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2018;56(7):1035-1045. - PubMed
-
- Franchini M, Mannucci PM. Primary hyperfibrinolysis: facts and fancies. Thromb Res. 2018;166:71-75. - PubMed
-
- Riley RS, Gilbert AR, Dalton JB, Pai S, McPherson RA. Widely used types and clinical applications of D-dimer assay. Lab Med. 2016;47(2):90-102. - PubMed
-
- Linkins LA, Takach Lapner S. Review of D-dimer testing: good, bad, and ugly. Int J Lab Hematol. 2017;39(Suppl 1):98-103. - PubMed
-
- Johnson ED, Schell JC, Rodgers GM. The D-dimer assay. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(7):833-839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

