A Phase II Basket Trial of Dual Anti-CTLA-4 and Anti-PD-1 Blockade in Rare Tumors (DART SWOG 1609 Cohort 47) in Patients with Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
- PMID: 37882676
- PMCID: PMC10842092
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-2293
A Phase II Basket Trial of Dual Anti-CTLA-4 and Anti-PD-1 Blockade in Rare Tumors (DART SWOG 1609 Cohort 47) in Patients with Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
Abstract
Purpose: The efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade in gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN) remains uncertain. We report the results of the GTN cohort of SWOG S1609 dual anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 blockade in rare tumors (DART).
Patients and methods: This prospective, open-label phase II trial evaluated ipilimumab plus nivolumab across multiple rare tumor cohorts, including GTN. Eligible patients received nivolumab 240 mg, i.v. every 2 weeks and ipilimumab 1 mg/kg i.v. every 6 weeks. The primary endpoint was overall response rate [ORR; complete response (CR) + partial response (PR)] by quantitative serum beta human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG); secondary endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and toxicity.
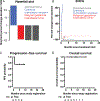
Results: Four patients with refractory GTN enrolled and received therapy. At 11 months of ongoing follow-up, 3 of 4 patients responded [ORR = 75% (CR, 25%, n = 1, tumor mutation burden = 1 mutation/megabase; PD-L1 tumor proportion score = 50%); PR, 50%, n = 2)]. Responders included malignant gestational trophoblastic neoplasm (n = 1, CR, PFS 11+ months) and choriocarcinoma (n = 2, both PRs, PFS 10+ and 6+ months). One patient with epithelioid trophoblastic tumor experienced disease progression. The 6-month PFS was 75% [95% confidence interval (CI), 43%-100%], and the median PFS was not reached (range, 35-339+ days); all 4 patients were alive at last follow-up. Two patients experienced grade 3 immune-related toxicity (arthralgia and colitis); there were no grade ≥4 events.
Conclusions: Ipilimumab plus nivolumab demonstrated efficacy in chemotherapy-refractory GTN, an ultra-rare cancer affecting young women. Three of 4 patients achieved ongoing objective responses with a reasonable safety profile at 6-11+ months.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Patel reported grants or contracts from Amgen, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Fate Therapeutics, Gilead, Iovance, Merck, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, SQZ Biotechnologies; consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Certis, Eli Lilly, Jazz, Genentech, Illumina, Merck, Pfizer, Rakuten, Tempus
Dr. Othus reported support from grant award NIH/NCI/NCTN U010CA180819; consulting fee from Merck, Biosight; participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for Celgene, Glycomimetics, Grifols
Dr. Chae reported research grants from Research Grant: Abbvie, BMS, Biodesix, Freenome, Predicine; honoraria from Roche/Genentech, AstraZeneca, Foundation Medicine, Neogenomics, Guardant Health, Boehringher Ingelheim, Biodesix, Immuneoncia, Lilly Oncology, Merck, Takeda, Lunit, Jazz Pharmaceutical, Tempus, BMS, Regeneron, NeoImmunTech, Esai; participating in Advisory Boards for Roche/Genentech, AstraZeneca, Foundation Medicine, Neogenomics, Guardant Health, Boehringher Ingelheim, Biodesix, Immuneoncia, Lilly Oncology, Merck, Takeda, Lunit, Jazz Pharmaceutical, Tempus, BMS, Regeneron, NeoImmunTech, Esai
Dr. Dennis reported consulting fees from MJH Life Sciences
Dr. Gordon reported grant funding: FP00013216_SA001.
Dr. Mutch reported none.
Dr. Samlowski reported support from grant award 5U10CA035421; honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb; and participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board with Immunicum.
Dr. Robinson reported none.
Dr. Sharon reported none
Dr. Ryan reported grants or contracts (payment to institution) from Ayala, Bristol-Meyer Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Deciphera, Exelixis, Genentech, Novartis, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Merck, Nektar, Pfizer, Xynomic, PF Argentum IP Holdings LLC, Rain Therapeutics, Shasqi, PTC Therapeutics, NiKang Therapeutics; consulting fees from Synox, Daiichi Sankyo, AVEO, Exelixis, Astra Zeneca, Bristol-Meyer Squibb; Payment for expert testimony from Pfizer, GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim (Payments to him by representative counsel)
Ms. Lopez reported none
Ms. Plets reported none.
Dr. Blanke reported support from National Institutes of Health
Dr. Kurzrock reported research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim, Debiopharm, Foundation Medicine, Genentech, Grifols, Guardant, Incyte, Konica Minolta, Medimmune, Merck Serono, Omniseq, Pfizer, Sequenom, Takeda, and TopAlliance and from the NCI; as well as consultant and/or speaker fees and/or advisory board/consultant for Actuate Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bicara Therapeutics, Inc., Biological Dynamics, Caris, Datar Cancer Genetics, Daiichi, EISAI, EOM Pharmaceuticals, Iylon, LabCorp, Merck, NeoGenomics, Neomed, Pfizer, Prosperdtx, Regeneron, Roche, TD2/Volastra, Turning Point Therapeutics, X-Biotech; has an equity interest in CureMatch Inc. and IDbyDNA; serves on the Board of CureMatch and CureMetrix, and is a co-founder of CureMatch.
Figures
References
-
- Abu-Rustum NR, Yashar CM, Bean S, Bradley K, Campos SM, Chon HS, et al. Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia, Version 2.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019. Nov;17(11):1374–91. - PubMed
-
- Anantharaju A, Pallavi VR, Bafna UD, Rathod PS, R VC, K S, et al. Role of salvage therapy in chemo resistant or recurrent high-risk gestational trophoblastic neoplasm. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2019. Mar;29(3):547–53. - PubMed
-
- Hoekstra AV, Lurain JR, Rademaker AW, Schink JC. Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia. 2008;112(2):8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials