Somatic estrogen receptor α mutations that induce dimerization promote receptor activity and breast cancer proliferation
- PMID: 37883178
- PMCID: PMC10760953
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI163242
Somatic estrogen receptor α mutations that induce dimerization promote receptor activity and breast cancer proliferation
Abstract
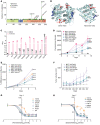
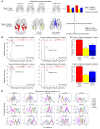
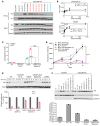
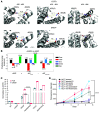
Physiologic activation of estrogen receptor α (ERα) is mediated by estradiol (E2) binding in the ligand-binding pocket of the receptor, repositioning helix 12 (H12) to facilitate binding of coactivator proteins in the unoccupied coactivator binding groove. In breast cancer, activation of ERα is often observed through point mutations that lead to the same H12 repositioning in the absence of E2. Through expanded genetic sequencing of breast cancer patients, we identified a collection of mutations located far from H12 but nonetheless capable of promoting E2-independent transcription and breast cancer cell growth. Using machine learning and computational structure analyses, this set of mutants was inferred to act distinctly from the H12-repositioning mutants and instead was associated with conformational changes across the ERα dimer interface. Through both in vitro and in-cell assays of full-length ERα protein and isolated ligand-binding domain, we found that these mutants promoted ERα dimerization, stability, and nuclear localization. Point mutations that selectively disrupted dimerization abrogated E2-independent transcriptional activity of these dimer-promoting mutants. The results reveal a distinct mechanism for activation of ERα function through enforced receptor dimerization and suggest dimer disruption as a potential therapeutic strategy to treat ER-dependent cancers.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Drug therapy; Endocrinology; Oncology; Sex hormones.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

