Combined thermal ablation and liposomal granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulation factor increases immune cell trafficking in a small animal tumor model
- PMID: 37883367
- PMCID: PMC10602257
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293141
Combined thermal ablation and liposomal granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulation factor increases immune cell trafficking in a small animal tumor model
Abstract
Purpose: To characterize intratumoral immune cell trafficking in ablated and synchronous tumors following combined radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and systemic liposomal granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulation factor (lip-GM-CSF).
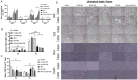
Methods: Phase I, 72 rats with single subcutaneous R3230 adenocarcinoma were randomized to 6 groups: a) sham; b&c) free or liposomal GM-CSF alone; d) RFA alone; or e&f) combined with blank liposomes or lip-GM-CSF. Animals were sacrificed 3 and 7 days post-RFA. Outcomes included immunohistochemistry of dendritic cells (DCs), M1 and M2 macrophages, T-helper cells (Th1) (CD4+), cytotoxic T- lymphocytes (CTL) (CD8+), T-regulator cells (T-reg) (FoxP3+) and Fas Ligand activated CTLs (Fas-L+) in the periablational rim and untreated index tumor. M1/M2, CD4+/CD8+ and CD8+/FoxP3+ ratios were calculated. Phase II, 40 rats with double tumors were randomized to 4 groups: a) sham, b) RFA, c) RFA-BL and d) RFA-lip-GM-CSF. Synchronous untreated tumors collected at 7d were analyzed similarly.
Results: RFA-lip-GMCSF increased periablational M1, CTL and CD8+/FoxP3+ ratio at 3 and 7d, and activated CTLs 7d post-RFA (p<0.05). RFA-lip-GMSCF also increased M2, T-reg, and reduced CD4+/CD8+ 3 and 7d post-RFA respectively (p<0.05). In untreated index tumor, RFA-lip-GMCSF improved DCs, M1, CTLs and activated CTL 7d post-RFA (p<0.05). Furthermore, RFA-lip-GMSCF increased M2 at 3 and 7d, and T-reg 7d post-RFA (p<0.05). In synchronous tumors, RFA-BL and RFA-lip-GM-CSF improved DC, Th1 and CTL infiltration 7d post-RFA.
Conclusion: Systemic liposomal GM-CSF combined with RFA improves intratumoral immune cell trafficking, specifically populations initiating (DC, M1) and executing (CTL, FasL+) anti-tumor immunity. Moreover, liposomes influence synchronous untreated metastases increasing Th1, CTL and DCs infiltration.
Copyright: © 2023 Moussa et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
VAB has patents on the PD-1 pathway licensed by Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Merck, EMD-Serono, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Novartis and Dako. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

