Bridging population pharmacokinetic and semimechanistic absorption modeling of APX3330
- PMID: 37884051
- PMCID: PMC10787204
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.13061
Bridging population pharmacokinetic and semimechanistic absorption modeling of APX3330
Abstract
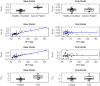
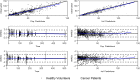
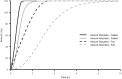
APX3330 ((2E)-2-[(4,5-dimethoxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxo-1,4-cyclohexadien-1-yl)methylene]-undecanoic acid), a selective inhibitor of APE1/Ref-1, has been investigated in treatment of hepatitis, cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and macular edema. APX3330 is administered orally as a quinone but is rapidly converted to the hydroquinone form. This study describes the pharmacokinetics of APX3330 and explores effect of food on absorption. Total plasma quinone concentrations of APX3330 were obtained following oral administration from studies in healthy Japanese male subjects (single dose-escalation; multiple-dose; food-effect) and patients with cancer patients. Nonlinear mixed effects modeling was performed using Monolix to estimate pharmacokinetic parameters and assess covariate effects. To further evaluate the effect of food on absorption, a semi-physiologic pharmacokinetic model was developed in Gastroplus to delineate effects of food on dissolution and absorption. A two-compartment, first order absorption model with lag time best described plasma concentration-time profiles from 49 healthy Japanese males. Weight was positively correlated with apparent clearance (CL/F) and volume. Administration with food led to an 80% higher lag time. CL/F was 41% higher in the cancer population. The semi-physiologic model indicates a switch from dissolution-rate control of absorption in the fasted-state to gastric emptying rate determining absorption rate in the fed-state. Oral clearance of APX3330 is higher in patients with cancer than healthy Japanese males, possibly due to reduced serum albumin in patients with cancer. Delayed APX3330 absorption with food may be related to higher conversion to the more soluble but less permeable hydroquinone form in the gastrointestinal tract. Future work should address pharmacokinetic differences between APX3330 quinone and hydroquinone forms.
© 2023 The Authors. CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
M.R.K. has licensed APX3330 through Indiana University Research and Technology Corporation to Apexian Pharmaceuticals LLC. R.M. is an employee of Apexian Pharmaceuticals. Apexian Pharmaceuticals had neither control nor oversight of the studies, interpretation, input, or presentation of the data in this manuscript. Apexian Pharmaceuticals has licensed APX3330 to Ocuphire Pharma for clinical trial studies in diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. M.R.K. is a co‐founder of Apexian Pharmaceuticals and is a medical consultant to Ocuphire Pharma who had neither control nor oversight of the studies, input, interpretation, or presentation of the data in this manuscript. All other authors declared no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population pharmacokinetics of losmapimod in healthy subjects and patients with rheumatoid arthritis and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013 Mar;52(3):187-98. doi: 10.1007/s40262-012-0025-6. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013. PMID: 23254770 Clinical Trial.
-
Diabetes mellitus reduces the clearance of atorvastatin lactone: results of a population pharmacokinetic analysis in renal transplant recipients and in vitro studies using human liver microsomes.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012 Sep 1;51(9):591-606. doi: 10.2165/11632690-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012. PMID: 22775412 Clinical Trial.
-
Population Pharmacokinetic Modelling of Acetaminophen and Ibuprofen: the Influence of Body Composition, Formulation and Feeding in Healthy Adult Volunteers.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2022 Jul;47(4):497-507. doi: 10.1007/s13318-022-00766-9. Epub 2022 Apr 2. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2022. PMID: 35366213 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine in two slow release formulations: pronounced lag-time after a high fat breakfast.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002 Jun;53(6):582-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.01599.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12047482 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Model-Based Analysis of Cannabidiol Dose-Exposure Relationship and Bioavailability.Pharmacotherapy. 2020 Apr;40(4):291-300. doi: 10.1002/phar.2377. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Pharmacotherapy. 2020. PMID: 32058609
References
-
- Zou GM, Karikari C, Kabe Y, Handa H, Anders RA, Maitra A. The Ape‐1/Ref‐1 redox antagonist E3330 inhibits the growth of tumor endothelium and endothelial progenitor cells: therapeutic implications in tumor angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2009;219:209‐218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01CA254110/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA231267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA205166/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA205166/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA167291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002529/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA274304/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA231267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA082709/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA254110/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL140961/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY031939/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA167291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

