Antibody-directed extracellular proximity biotinylation reveals that Contactin-1 regulates axo-axonic innervation of axon initial segments
- PMID: 37884508
- PMCID: PMC10603070
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42273-8
Antibody-directed extracellular proximity biotinylation reveals that Contactin-1 regulates axo-axonic innervation of axon initial segments
Abstract
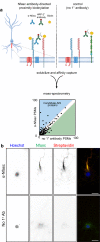
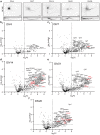
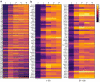
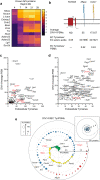
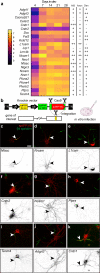
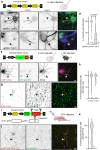
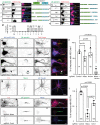
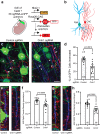
Axon initial segment (AIS) cell surface proteins mediate key biological processes in neurons including action potential initiation and axo-axonic synapse formation. However, few AIS cell surface proteins have been identified. Here, we use antibody-directed proximity biotinylation to define the cell surface proteins in close proximity to the AIS cell adhesion molecule Neurofascin. To determine the distributions of the identified proteins, we use CRISPR-mediated genome editing for insertion of epitope tags in the endogenous proteins. We identify Contactin-1 (Cntn1) as an AIS cell surface protein. Cntn1 is enriched at the AIS through interactions with Neurofascin and NrCAM. We further show that Cntn1 contributes to assembly of the AIS extracellular matrix, and regulates AIS axo-axonic innervation by inhibitory basket cells in the cerebellum and inhibitory chandelier cells in the cortex.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Antibody-directed extracellular proximity biotinylation reveals Contactin-1 regulates axo-axonic innervation of axon initial segments.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 6:2023.03.06.531378. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.06.531378. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 26;14(1):6797. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42273-8. PMID: 36945454 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

