Identification of antigens in the Trichinella spiralis extracellular vesicles for serological detection of early stage infection in swine
- PMID: 37884927
- PMCID: PMC10604534
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-023-06013-7
Identification of antigens in the Trichinella spiralis extracellular vesicles for serological detection of early stage infection in swine
Abstract
Background: Several studies have reported the roles of Trichinella spiralis extracellular vesicles in immune regulation and pathogen diagnosis. Currently, the T. spiralis muscle larvae excretory/secretory product (Ts-ML-ES) is the antigen recommended by the International Commission on Trichinellosis (ICT) for serological diagnosis of trichinellosis. However, it can only be used to detect middle and late stages of infections, and cross-reactions with other parasite detections occur. Therefore, there is a need to identify antigens for specific detection of early stage trichinellosis.
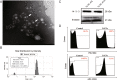
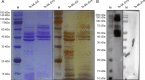
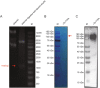
Methods: Extracellular vesicles of T. spiralis muscle larvae (Ts-ML-EVs) were isolated by ultracentrifugation and characterized by transmission electron microscopy, nanoparticle tracking analysis, flow cytometry and western blot. Ts-ML-EVs protein profiles were analyzed by LC-MS/MS proteomics for identification of potential antigens (Ts-TTPA). Ts-TTPA were cloned into pMAL-c5X vector and expressed as recombinant proteins for evaluation of potential as detected antigens by western blot and ELISA.
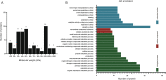
Results: Isolated Ts-ML-EVs were round or elliptic (with diameters between 110.1 and 307.6 nm), showing a bilayer membrane structure. The specific surface markers on the Ts-ML-EVs were CD81, CD63, enolase and the 14-3-3 protein. A total of 53 proteins were identified by LC-MS/MS, including a variety of molecules that have been reported as potential detection and vaccine candidates. The cDNA of Ts-TTPA selected in this study has a total length of 1152 bp, encoding 384 amino acids with a molecular weight of 44.19 kDa. It contains a trypsin domain and can be recognized by anti-His antibody. It reacted with swine sera infected with 10,000 T. spiralis at 15, 25, 35 and 60 days post-infection (dpi). At 10 μg/ml, this antigen could detect T. spiralis antibodies from the swine sera at 13 dpi. There were no cross-reactions with the swine sera infected with other parasites including Clonorchis sinensis, Toxoplasma gondii, Taenia suis, Ascaris suis and Trichuris suis.
Conclusions: This study identifies potential early stage detection antigens and more thoroughly characterizes a serine protease domain-containing protein. Extracellular vesicle proteins may be explored as effective antigens for the early stage detection of trichinellosis.
Keywords: Detection antigens of early stage; Extracellular vesicle; Proteomics; Trichinella spiralis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[The usefulness of ELISA test for early serological detection of Trichinella spp. infection in pigs].Wiad Parazytol. 2007;53(2):149-51. Wiad Parazytol. 2007. PMID: 17912813 Polish.
-
Use of ELISA and Western blot for serological detection of antibodies to E-S antigens of Trichinella spiralis muscle larvae in sera of swine experimentally infected with Trichinella spiralis.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2018 Sep;203:13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2018.07.010. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2018. PMID: 30243368
-
Application of a recombinant novel trypsin from Trichinella spiralis for serodiagnosis of trichinellosis.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Jan 4;17(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06067-7. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38178167 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccines against Trichinella spiralis: Progress, challenges and future prospects.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018 Dec;65(6):1447-1458. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12917. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018. PMID: 29873198 Review.
-
Workshop on a detailed characterization of Trichinella spiralis antigens: a platform for future studies on antigens and antibodies to this parasite.Parasite Immunol. 1996 Jun;18(6):273-84. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3024.1996.d01-103.x. Parasite Immunol. 1996. PMID: 9229380 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Genomic and Transcriptomic Resources for Trichinella pseudospiralis and T. spiralis to Underpin the Discovery of Molecular Differences between Stages and Species.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 5;25(13):7366. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137366. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000473 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of extracellular vesicles in pathogens with special focus on human extracellular protozoan parasites.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2024 Sep 23;119:e240073. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760240073. eCollection 2024. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2024. PMID: 39319874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precocious Eimeria magna transgenically expressing RHDV P2 subdomain induces immune responses in rabbits.NPJ Vaccines. 2025 Jul 24;10(1):167. doi: 10.1038/s41541-025-01223-9. NPJ Vaccines. 2025. PMID: 40707472 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

