Repeatability of Quantitative Knee Cartilage T1, T2, and T1ρ Mapping With 3D-MRI Fingerprinting
- PMID: 37885320
- PMCID: PMC11045656
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.29068
Repeatability of Quantitative Knee Cartilage T1, T2, and T1ρ Mapping With 3D-MRI Fingerprinting
Abstract
Background: Three-dimensional MR fingerprinting (3D-MRF) techniques have been recently described for simultaneous multiparametric mapping of knee cartilage. However, investigation of repeatability remains limited.
Purpose: To assess the intra-day and inter-day repeatabilities of knee cartilage T1, T2, and T1ρ maps using a 3D-MRF sequence for simultaneous measurement.
Study type: Prospective.
Subjects: Fourteen healthy subjects (35.4 ± 9.3 years, eight males), scanned on Day 1 and Day 7.
Field strength/sequence: 3 T/3D-MRF, T1, T2, and T1ρ maps.
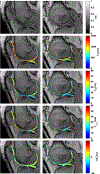
Assessment: The acquisition of 3D-MRF cartilage (simultaneous acquisition of T1, T2, and T1ρ maps) were acquired using a dictionary pattern-matching approach. Conventional cartilage T1, T2, and T1ρ maps were acquired using variable flip angles and a modified 3D-Turbo-Flash sequence with different echo and spin-lock times, respectively, and were fitted using mono-exponential models. Each sequence was acquired on Day 1 and Day 7 with two scans on each day.
Statistical tests: The mean and SD for cartilage T1, T2, and T1ρ were calculated in five manually segmented regions of interest (ROIs), including lateral femur, lateral tibia, medial femur, medial tibia, and patella cartilages. Intra-subject and inter-subject repeatabilities were assessed using coefficient of variation (CV) and intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC), respectively, on the same day and among different days. Regression and Bland-Altman analysis were performed to compare maps between the conventional and 3D-MRF sequences.
Results: The CV in all ROIs was lower than 7.4%, 8.4%, and 7.5% and the ICC was higher than 0.56, 0.51, and 0.52 for cartilage T1, T2, and T1ρ, respectively. The MRF results had a good agreement with the conventional methods with a linear regression slope >0.61 and R2 > 0.59.
Conclusion: The 3D-MRF sequence had high intra-subject and inter-subject repeatabilities for simultaneously measuring knee cartilage T1, T2, and T1ρ with good agreement with conventional sequences.
Evidence level: 1 TECHNICAL EFFICACY: Stage 1.
Keywords: MRF; knee cartilage; quantitative mapping; repeatability.
© 2023 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures





References
-
- Vos T, Barber RM, Bell B, Bertozzi-Villa A, Biryukov S, Bolliger I, Charlson F, Davis A, Degenhardt L, Dicker D, Duan L. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. The lancet. 2015. Aug 22;386(9995):743–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guermazi A, Alizai H, Crema MD, Trattnig S, Regatte RR, Roemer FW. Compositional MRI techniques for evaluation of cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 2015;23(10):1639–1653 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01-AR078308-01A1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR076328/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR078308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41EB017183/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR076985/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB017183/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR076985/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR076328/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- Center of Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research
- R01 AR076328/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR076985/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR078308-01A1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P41EB017183/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- NIBIB Biomedical Technology Resource Center
- NYU Grossman School of Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

