Protective effect and mechanism of procyanidin B2 against hypoxic injury of cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 37885736
- PMCID: PMC10598540
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21309
Protective effect and mechanism of procyanidin B2 against hypoxic injury of cardiomyocytes
Abstract
Background: Cardiomyocyte ischemia and hypoxia are important causes of oxidative stress damage and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in coronary heart disease (CHD). Epidemiological investigation has shown that eating more plant-based foods, such as vegetables and fruits, may significantly decrease the risk of CHD. As natural antioxidants, botanicals have fewer toxic side effects than chemical drugs and have great potential for development. Procyanidin B2 (PB2) is composed of flavan-3-ol and epicatechin and has been reported to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. However, whether PB2 exerts protective effects on hypoxic cardiomyocytes has remained unclear. This study aimed to explore the protective effect of PB2 against cardiomyocyte hypoxia and to provide new treatment strategies and ideas for myocardial ischemia and hypoxia in CHD.
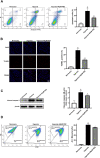
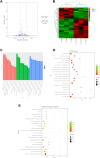
Methods and results: A hypoxic cardiomyocyte model was constructed, and a CCK-8 assay proved that PB2 had a protective effect on cardiomyocytes in a hypoxic environment. DCFH fluorescence staining, DHE staining, and BODIPY lipid oxidation assessment revealed that PB2 reduced the oxidative stress levels of cardiomyocytes under hypoxic conditions. TUNEL staining, Annexin V/PI fluorescence flow cytometry, and Western blot analysis of the expression of the apoptosis marker protein cleaved caspase-3 confirmed that PB2 reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis under hypoxic conditions. JC-1 staining indicated that PB2 reduced the mitochondrial membrane potential of cardiomyocytes under hypoxia. In addition, transcriptomic analysis proved that the expression of 158 genes in cardiomyocytes was significantly changed after PB2 was added during hypoxia, of which 53 genes were upregulated and 105 genes were downregulated. GO enrichment analysis demonstrated that the activity of cytokines, extracellular matrix proteins and other molecules was changed significantly in the biological process category. KEGG enrichment analysis showed that the IL-17 signaling pathway and JAK-STAT signaling pathway underwent significant changes. We also performed metabolomic analysis and found that the levels of 51 metabolites were significantly changed after the addition of PB2 to cardiomyocytes during hypoxia. Among them, 39 metabolites exhibited increased levels, while 12 metabolites exhibited decreased levels. KEGG enrichment analysis showed that cysteine and methionine metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism and other metabolic pathways underwent remarkable changes.
Conclusion: This study proves that PB2 can reduce the oxidative stress and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes during hypoxia to play a protective role. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses preliminarily revealed signaling pathways and metabolic pathways that are related to its protective mechanism. These findings lay a foundation for further research on the role of PB2 in the treatment of CHD and provide new ideas and new perspectives for research on PB2 in the treatment of other diseases.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cardiomyocyte hypoxia; Coronary heart disease; Oxidative stress; Procyanidin B2.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Metabolomic Analysis of the Ameliorative Effect of Enhanced Proline Metabolism on Hypoxia-Induced Injury in Cardiomyocytes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Nov 26;2020:8866946. doi: 10.1155/2020/8866946. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33294127 Free PMC article.
-
[Role and related mechanism of Mst-1 on regulating hypoxic reoxygenation induced autophagy and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes of mouse].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2020 Dec 24;48(12):1060-1069. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20201102-00873. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33355751 Chinese.
-
PHLPP2 downregulation protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced injury through reinforcing Nrf2/ARE antioxidant signaling.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Dec 1;314:108848. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108848. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 31610156
-
Propofol inhibits myocardial injury induced by microvesicles derived from hypoxia-reoxygenated endothelial cells via lncCCT4-2/CCT4 signaling.Biol Res. 2023 May 5;56(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40659-023-00428-3. Biol Res. 2023. PMID: 37143143 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-324/SOCS3 Axis Protects Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury and Regulates Myocardial Ischemia via TNF/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Int Heart J. 2020 Nov 28;61(6):1258-1269. doi: 10.1536/ihj.19-687. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Int Heart J. 2020. PMID: 33191336
Cited by
-
In Vitro Culture of Human Dermal Fibroblasts on Novel Electrospun Polylactic Acid Fiber Scaffolds Loaded with Encapsulated Polyepicatechin Physical Gels.Gels. 2024 Sep 20;10(9):601. doi: 10.3390/gels10090601. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39330203 Free PMC article.
-
Nitidine Chloride Alleviates Hypoxic Stress via PINK1-Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy in the Mammary Epithelial Cells of Milk Buffalo.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;14(20):3016. doi: 10.3390/ani14203016. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olivetti G., Abbi R., Quaini F., Kajstura J., Cheng W., Nitahara J.A., Quaini E., Di Loreto C., Beltrami C.A., Krajewski S., Reed J.C., Anversa P. Apoptosis in the failing human heart. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;336:1131–1141. - PubMed
-
- Hafstad A.D., Nabeebaccus A.A., Shah A.M. Novel aspects of ROS signalling in heart failure. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2013;108:359. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

