The role of FGFR inhibitors in the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma-unveiling the future challenges in drug therapy
- PMID: 37886210
- PMCID: PMC10598302
- DOI: 10.21037/hbsn-23-411
The role of FGFR inhibitors in the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma-unveiling the future challenges in drug therapy
Keywords: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA); chemotherapy; fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor (FGFR inhibitor); mutation; tumor immune microenvironment (TIME).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The author has completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://hbsn.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/hbsn-23-411/coif). The author reports that this work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (KAKENHI: 21K07184), and a grant from Smoking Research Foundation.
Figures
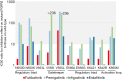
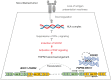
Comment on
-
Futibatinib for FGFR2-Rearranged Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jan 19;388(3):228-239. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206834. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 36652354 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Oh D-Y, He AR, Qin S, et al. Durvalumab plus Gemcitabine and Cisplatin in Advanced Biliary Tract Cancer. NEJM Evid 2022;1. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
