This is a preprint.
Molecular fingerprinting of biological nanoparticles with a label-free optofluidic platform
- PMID: 37886549
- PMCID: PMC10602063
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3309306/v1
Molecular fingerprinting of biological nanoparticles with a label-free optofluidic platform
Update in
-
Molecular fingerprinting of biological nanoparticles with a label-free optofluidic platform.Nat Commun. 2024 May 15;15(1):4109. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48132-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38750038 Free PMC article.
Abstract
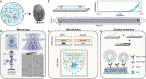
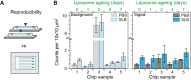
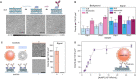
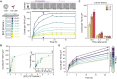
Label-free detecting multiple analytes in a high-throughput fashion has been one of the long-sought goals in biosensing applications. Yet, for all-optical approaches, interfacing state-of-the-art label-free techniques with microfluidics tools that can process small volumes of sample with high throughput, and with surface chemistry that grants analyte specificity, poses a critical challenge to date. Here, we introduce an optofluidic platform that brings together state-of-the-art digital holography with PDMS microfluidics by using supported lipid bilayers as a surface chemistry building block to integrate both technologies. Specifically, this platform fingerprints heterogeneous biological nanoparticle populations via a multiplexed label-free immunoaffinity assay with single particle sensitivity. Herein, we first thoroughly characterise the robustness and performance of the platform, and then apply it to profile four distinct ovarian cell-derived extracellular vesicle populations over a panel of surface protein biomarkers, thus developing a unique biomarker fingerprint for each cell line. We foresee that our approach will find many applications where routine and multiplexed characterisation of biological nanoparticles is required.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; holography; immunoassays; label-free imaging; microfluidics; multiplexing; supported lipid bilayer.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

