The Hypothalamus of the Beaked Whales: The Paraventricular, Supraoptic, and Suprachiasmatic Nuclei
- PMID: 37887029
- PMCID: PMC10604544
- DOI: 10.3390/biology12101319
The Hypothalamus of the Beaked Whales: The Paraventricular, Supraoptic, and Suprachiasmatic Nuclei
Abstract
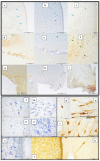
The hypothalamus is the body's control coordinating center. It is responsible for maintaining the body's homeostasis by directly influencing the autonomic nervous system or managing hormones. Beaked whales are the longest divers among cetaceans and their brains are rarely available for study. Complete hypothalamic samples from a female Cuvier's beaked whale and a male Blainville's beaked whale were processed to investigate the paraventricular (PVN) and supraoptic (SON) nuclei, using immunohistochemical staining against vasopressin. The PVN occupied the preoptic region, where it reached its maximum size, and then regressed in the anterior or suprachiasmatic region. The SON was located from the preoptic to the tuberal hypothalamic region, encompassing the optical structures. It was composed of a retrochiasmatic region (SONr), which bordered and infiltrated the optic tracts, and a principal region (SONp), positioned more medially and dorsally. A third vasopressin-positive nucleus was also detected, i.e., the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which marked the end of the SON. This is the first description of the aforementioned nuclei in beaked whales-and in any marine mammals-as well as their rostro-caudal extent and immunoreactivity. Moreover, the SCN has been recognized for the first time in any marine mammal species.
Keywords: beaked whales; hypothalamus; paraventricular nucleus; suprachiasmatic nucleus; supraoptic nucleus; toothed whales.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Trackline and point detection probabilities for acoustic surveys of Cuvier's and Blainville's beaked whales.J Acoust Soc Am. 2013 Sep;134(3):2486-96. doi: 10.1121/1.4816573. J Acoust Soc Am. 2013. PMID: 23968046
-
Galanin immunoreactive neurons in the human hypothalamus: colocalization with vasopressin-containing neurons.J Comp Neurol. 1990 Aug 15;298(3):265-80. doi: 10.1002/cne.902980302. J Comp Neurol. 1990. PMID: 1698834
-
Passive acoustic monitoring of beaked whale densities in the Gulf of Mexico.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 12;5:16343. doi: 10.1038/srep16343. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26559743 Free PMC article.
-
Development of the human hypothalamus.Neurochem Res. 1995 May;20(5):509-19. doi: 10.1007/BF01694533. Neurochem Res. 1995. PMID: 7643957 Review.
-
Lifespan changes in the human hypothalamus.Exp Gerontol. 1997 Jul-Oct;32(4-5):559-75. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(96)00162-3. Exp Gerontol. 1997. PMID: 9315457 Review.
Cited by
-
Salivary Biomarkers as a Predictive Factor in Anxiety, Depression, and Stress.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jun 26;47(7):488. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070488. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40728957 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paxinos G. The Rat Nervous System. 3rd ed. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2004.
-
- Schröder H., Moser N., Huggenberger S. The Mouse Hypothalamus. In: Schröder H., Moser N., Huggenberger S., editors. Neuroanatomy of the Mouse: An Introduction. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. pp. 205–230.
-
- Dudás B. Atlas of the Human Hypothalamus. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2021. Part I—Morphology of the human hypothalamus: Anatomy, blood supply, nuclei and pathways; pp. 1–24. - DOI
-
- Swaab D.F., editor. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Volume 79. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Nederlands: 2003. Chapter 8 Supraoptic and paraventricular nucleus (SON, PVN) pp. 163–237. - PubMed
-
- Kupfermann I. Hypothalamus and limbic system: Peptidergic neurons, homeostasis, and emotional behavior. In: Kandel E.R., Schwartz J.H., Jessell T.M., editors. Principles of the Neural Science. Elsiever; New York, NY, USA: 1991. pp. 735–749. Chapter 47.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

