Thermal Transport and Rheological Properties of Hybrid Nanofluids Based on Vegetable Lubricants
- PMID: 37887889
- PMCID: PMC10609595
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13202739
Thermal Transport and Rheological Properties of Hybrid Nanofluids Based on Vegetable Lubricants
Abstract
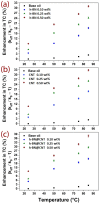
Nanofluids based on vegetal oil with different wt.% of carbon nanotubes (CNT), hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), and its hybrid (h-BN@CNT) were produced to investigate the effects of these nano-additives on the thermal conductivity and rheological properties of nanofluids. Stable suspensions of these oil/nanostructures were produced without the use of stabilizing agents. The dispersed nanostructures were investigated by SEM, EDS, XRD, and XPS, while the thermal conductivity and rheological characteristics were studied by a transient hot-wire method and steady-state flow tests, respectively. Increases in thermal conductivity of up to 39% were observed for fluids produced with 0.5 wt.% of the hybrid nanomaterials. As for the rheological properties, it was verified that both the base fluid and the h-BN suspensions exhibited Newtonian behavior, while the presence of CNT modified this tendency. This change in behavior is attributed to the hydrophobic character of both CNT and the base oil, while h-BN nanostructures have lip-lip "bonds", giving it a partial ionic character. However, the combination of these nanostructures was fundamental for the synergistic effect on the increase of thermal conductivity with respect to their counterparts.
Keywords: hybrid nanofluids; rheological properties; thermal conductivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Taha-Tijerina J., Ribeiro H., Aviña K., Martínez J.M., Godoy A.P., Cremonezzi J.M.d.O., Luciano M.A., Gimenes Benega M.A., Andrade R.J.E., Fechine G.J.M., et al. Thermal Conductivity Performance of 2D h-BN/MoS2/-Hybrid Nanostructures Used on Natural and Synthetic Esters. Nanomaterials. 2020;10:1160. doi: 10.3390/nano10061160. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Salah N., Abdel-wahab M.S., Alshahrie A., Alharbi N.D., Khan Z.H. Carbon nanotubes of oil fly ash as lubricant additives for different base oils and their tribology performance. RSC Adv. 2017;7:40295–40302. doi: 10.1039/C7RA07155H. - DOI
-
- Taha-Tijerina J.J., Aviña K., Ulloa-Castillo N.A., Melo-Maximo D.V. Thermal Transport and Physical Characteristics of Silver-Reinforced Biodegradable Nanolubricant. Sustainability. 2023;15:8795. doi: 10.3390/su15118795. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

