Breast Cancer Tissue Explants: An Approach to Develop Personalized Therapy in Public Health Services
- PMID: 37888132
- PMCID: PMC10608341
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13101521
Breast Cancer Tissue Explants: An Approach to Develop Personalized Therapy in Public Health Services
Abstract
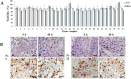
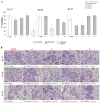
Breast cancer is one of the main causes of death worldwide. Lately, there is great interest in developing methods that assess individual sensitivity and/or resistance of tumors to antineoplastics to provide personalized therapy for patients. In this study we used organotypic culture of human breast tumor slices to predict the experimental effect of antineoplastics on the viability of tumoral tissue. Samples of breast tumor were taken from 27 patients with clinically advanced breast cancer; slices were obtained and incubated separately for 48 h with paclitaxel, docetaxel, epirubicin, 5-fluorouracil, cyclophosphamide, and cell culture media (control). We determined an experimental tumor sensitivity/resistance (S/R) profile by evaluating tissue viability using the Alamar Blue® metabolic test, and by structural viability (histopathological analyses, necrosis, and inflammation). These parameters were related to immunohistochemical expression of the estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. The predominant histological type found was infiltrating ductal carcinoma (85.2%), followed by lobular carcinoma (7.4%) and mixed carcinoma (7.4%). Experimental drug resistance was related to positive hormone receptor status in 83% of samples treated with cyclophosphamide (p = 0.027). Results suggest that the tumor S/R profile can help to predict personalized therapy or optimize chemotherapeutic treatments in breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; chemotherapy; ex vivo; explants; tissue slices; treatment response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Cancer, Nota Descriptive. 2021. [(accessed on 5 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer.
-
- INEGI (Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía) Estadísticas a Propósito del día Mundial Contra el Cáncer (Datos Nacionales) 2021. [(accessed on 25 June 2022)]. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/saladeprensa/aproposito/2021/EAP_LUC....
-
- Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública . Aportaciones a la Salud de los Mexicanos. INSP; Cuernavaca, Mexico: 2017. pp. 59–75.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

