Placental Vessel Segmentation Using Pix2pix Compared to U-Net
- PMID: 37888333
- PMCID: PMC10607321
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging9100226
Placental Vessel Segmentation Using Pix2pix Compared to U-Net
Abstract
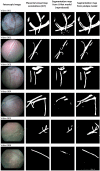
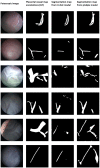
Computer-assisted technologies have made significant progress in fetoscopic laser surgery, including placental vessel segmentation. However, the intra- and inter-procedure variabilities in the state-of-the-art segmentation methods remain a significant hurdle. To address this, we investigated the use of conditional generative adversarial networks (cGANs) for fetoscopic image segmentation and compared their performance with the benchmark U-Net technique for placental vessel segmentation. Two deep-learning models, U-Net and pix2pix (a popular cGAN model), were trained and evaluated using a publicly available dataset and an internal validation set. The overall results showed that the pix2pix model outperformed the U-Net model, with a Dice score of 0.80 [0.70; 0.86] versus 0.75 [0.0.60; 0.84] (p-value < 0.01) and an Intersection over Union (IoU) score of 0.70 [0.61; 0.77] compared to 0.66 [0.53; 0.75] (p-value < 0.01), respectively. The internal validation dataset further validated the superiority of the pix2pix model, achieving Dice and IoU scores of 0.68 [0.53; 0.79] and 0.59 [0.49; 0.69] (p-value < 0.01), respectively, while the U-Net model obtained scores of 0.53 [0.49; 0.64] and 0.49 [0.17; 0.56], respectively. This study successfully compared U-Net and pix2pix models for placental vessel segmentation in fetoscopic images, demonstrating improved results with the cGAN-based approach. However, the challenge of achieving generalizability still needs to be addressed.
Keywords: fetal surgery; fetoscopy; generative artificial intelligence; twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome; vessel segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bano S., Vasconcelos F., Shepherd L.M., Poorten E.V., Vercauteren T., Ourselin S., David A.L., Deprest J., Stoyanov D. Deep placental vessel segmentation for fetoscopic mosaicking; Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Lima, Peru. 4–8 October 2020; pp. 763–773.
-
- Patnaik P., Khodee A., Vasam G., Mukherjee A., Salsabili S., Ukwatta E., Grynspan D., Chan A.D., Bainbridge S. Automated Detection of Maternal Vascular Malperfusion Lesions of the Placenta using Machine Learning. medRxiv. 2023:2023.2006. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources