Technosols Derived from Mining, Urban, and Agro-Industrial Waste for the Remediation of Metal(loid)-Polluted Soils: A Microcosm Assay
- PMID: 37888704
- PMCID: PMC10610840
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11100854
Technosols Derived from Mining, Urban, and Agro-Industrial Waste for the Remediation of Metal(loid)-Polluted Soils: A Microcosm Assay
Abstract
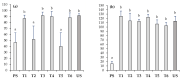
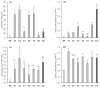
This study evaluated the effectiveness of six Technosols designed for the remediation of polluted soils (PS) by metal(loid)s at physicochemical, biological, and ecotoxicological levels and at a microcosm scale. Technosols T1-T6 were prepared by combining PS with a mix of organic and inorganic wastes from mining, urban, and agro-industrial activities. After two months of surface application of Technosols on polluted soils, we analysed the soil properties, metal(loid) concentration in total, soluble and bioavailable fractions, soil enzymatic activities, and the growth responses of Trifolium campestre and Lactuca sativa in both the Technosols and the underlying polluted soils. All Technosols improved the unfavourable conditions of polluted soils by neutralising acidity, increasing the OC, reducing the mobility of most metal(loid)s, and stimulating both the soil enzymatic activities and growths of T. campestre and L. sativa. The origin of organic waste used in the Technosols strongly conditioned the changes induced in the polluted soils; in this sense, the Technosols composed of pruning and gardening vermicompost (T3 and T6) showed greater reductions in toxicity and plant growth than the other Technosols composed with different organic wastes. Thus, these Technosols constitute a potential solution for the remediation of persistent polluted soils that should be applied in large-scale and long-term interventions to reinforce their feasibility as a cost-effective ecotechnology.
Keywords: Lactuca sativa; Trifolium campestre; potentially toxic elements; soil enzymes; soil pollution; toxicity bioassays; vegetation recovery; waste valorisation; waste-derived Technosols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Khelifi F., Melki A., Hamed Y., Adamo P., Caporale A.G. Environmental and Human Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soil, Sediments, and Ore-Processing Wastes from a Mining Area of Southwestern Tunisia. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2020;42:4125–4139. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00434-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Islam M.M., Sohag K., Alam M.M. Mineral Import Demand and Clean Energy Transitions in the Top Mineral-Importing Countries. Resour. Policy. 2022;78:102893. doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.102893. - DOI
-
- Watari T., Nansai K., Nakajima K. Major Metals Demand, Supply, and Environmental Impacts to 2100: A Critical Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021;164:105107. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105107. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

