Simvastatin in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19
- PMID: 37888913
- PMCID: PMC10755839
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2309995
Simvastatin in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of simvastatin in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is unclear.
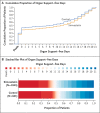
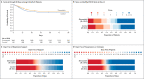
Methods: In an ongoing international, multifactorial, adaptive platform, randomized, controlled trial, we evaluated simvastatin (80 mg daily) as compared with no statin (control) in critically ill patients with Covid-19 who were not receiving statins at baseline. The primary outcome was respiratory and cardiovascular organ support-free days, assessed on an ordinal scale combining in-hospital death (assigned a value of -1) and days free of organ support through day 21 in survivors; the analyis used a Bayesian hierarchical ordinal model. The adaptive design included prespecified statistical stopping criteria for superiority (>99% posterior probability that the odds ratio was >1) and futility (>95% posterior probability that the odds ratio was <1.2).
Results: Enrollment began on October 28, 2020. On January 8, 2023, enrollment was closed on the basis of a low anticipated likelihood that prespecified stopping criteria would be met as Covid-19 cases decreased. The final analysis included 2684 critically ill patients. The median number of organ support-free days was 11 (interquartile range, -1 to 17) in the simvastatin group and 7 (interquartile range, -1 to 16) in the control group; the posterior median adjusted odds ratio was 1.15 (95% credible interval, 0.98 to 1.34) for simvastatin as compared with control, yielding a 95.9% posterior probability of superiority. At 90 days, the hazard ratio for survival was 1.12 (95% credible interval, 0.95 to 1.32), yielding a 91.9% posterior probability of superiority of simvastatin. The results of secondary analyses were consistent with those of the primary analysis. Serious adverse events, such as elevated levels of liver enzymes and creatine kinase, were reported more frequently with simvastatin than with control.
Conclusions: Although recruitment was stopped because cases had decreased, among critically ill patients with Covid-19, simvastatin did not meet the prespecified criteria for superiority to control. (REMAP-CAP ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02735707.).
Copyright © 2023 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
- doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2312635
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus (Covid-19) dashboard (https://covid19.who.int/).
-
- World Health Organization. Model list of essential medicines: 22nd list. 2021. (https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/345533/WHO-MHP-HPS-EML-2021....).
