Fusobacterium nucleatum and its metabolite hydrogen sulfide alter gut microbiota composition and autophagy process and promote colorectal cancer progression
- PMID: 37889013
- PMCID: PMC10714730
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02292-23
Fusobacterium nucleatum and its metabolite hydrogen sulfide alter gut microbiota composition and autophagy process and promote colorectal cancer progression
Abstract
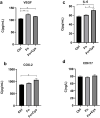
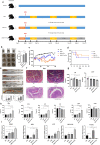
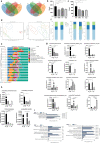
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second most common cancer in the world; the main treatment for CRC is immunosuppressive therapy, but this therapy is only effective for a small percentage of CRC patients, so there is an urgent need for a treatment with fewer side effects and higher efficacy. This study demonstrated that Fusobacterium nucleatum with increased abundance in CRC can regulate the autophagy process and disrupt normal intestinal microbiota by producing hydrogen sulfide, factors that may be involved in the development and progression of CRC. This study may provide a reference for future CRC treatment options that are efficient and have fewer side effects.
Keywords: Fusobacterium nucleatum; autophagy; colorectal cancer; gut microbiota; hydrogen sulfide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Kostic AD, Chun E, Robertson L, Glickman JN, Gallini CA, Michaud M, Clancy TE, Chung DC, Lochhead P, Hold GL, El-Omar EM, Brenner D, Fuchs CS, Meyerson M, Garrett WS. 2013. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 14:207–215. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gaines S, van Praagh JB, Williamson AJ, Jacobson RA, Hyoju S, Zaborin A, Mao J, Koo HY, Alpert L, Bissonnette M, Weichselbaum R, Gilbert J, Chang E, Hyman N, Zaborina O, Shogan BD, Alverdy JC. 2020. Western diet promotes intestinal colonization by collagenolytic microbes and promotes tumor formation after colorectal surgery. Gastroenterology 158:958–970. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

