Model-based characterization of the equilibrium dynamics of transcription initiation and promoter-proximal pausing in human cells
- PMID: 37889042
- PMCID: PMC10681744
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad843
Model-based characterization of the equilibrium dynamics of transcription initiation and promoter-proximal pausing in human cells
Abstract
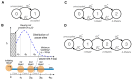
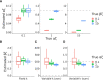
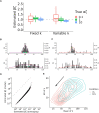
In metazoans, both transcription initiation and the escape of RNA polymerase (RNAP) from promoter-proximal pausing are key rate-limiting steps in gene expression. These processes play out at physically proximal sites on the DNA template and appear to influence one another through steric interactions. Here, we examine the dynamics of these processes using a combination of statistical modeling, simulation, and analysis of real nascent RNA sequencing data. We develop a simple probabilistic model that jointly describes the kinetics of transcription initiation, pause-escape, and elongation, and the generation of nascent RNA sequencing read counts under steady-state conditions. We then extend this initial model to allow for variability across cells in promoter-proximal pause site locations and steric hindrance of transcription initiation from paused RNAPs. In an extensive series of simulations, we show that this model enables accurate estimation of initiation and pause-escape rates. Furthermore, we show by simulation and analysis of real data that pause-escape is often strongly rate-limiting and that steric hindrance can dramatically reduce initiation rates. Our modeling framework is applicable to a variety of inference problems, and our software for estimation and simulation is freely available.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Kinetics of RNA polymerase initiation and pausing at the lambda late gene promoter in vivo.J Mol Biol. 1995 Dec 15;254(5):808-14. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0657. J Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7500352
-
Structural transitions in the transcription elongation complexes of bacterial RNA polymerase during σ-dependent pausing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Apr;40(7):3078-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1158. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22140106 Free PMC article.
-
A backtrack-inducing sequence is an essential component of Escherichia coli σ(70)-dependent promoter-proximal pausing.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Nov;78(3):636-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07347.x. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21382107 Free PMC article.
-
Pause & go: from the discovery of RNA polymerase pausing to its functional implications.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;46:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28363125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Transcriptional Pausing in Bacteria.J Mol Biol. 2019 Sep 20;431(20):4007-4029. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.07.017. Epub 2019 Jul 13. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31310765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of promoter-proximal pausing enabled a new layer of transcription control.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 24:rs.3.rs-2679520. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2679520/v1. Res Sq. 2023. PMID: 36993251 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Genome-wide dynamic nascent transcript profiles reveal that most paused RNA polymerases terminate.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 28:2025.03.27.645809. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.27.645809. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40196675 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Probabilistic and machine-learning methods for predicting local rates of transcription elongation from nascent RNA sequencing data.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 8;53(4):gkaf092. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf092. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39964478 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of promoter-proximal pausing enabled a new layer of transcription control.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 12:2023.02.19.529146. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.19.529146. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39416036 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
DNA-sequence and epigenomic determinants of local rates of transcription elongation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 23:2023.12.21.572932. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.21.572932. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 38187771 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Ptashne M., Gann A.. Transcriptional activation by recruitment. Nature. 1997; 386:569–577. - PubMed
-
- Krumm A., Meulia T., Brunvand M., Groudine M.. The block to transcriptional elongation within the human c-myc gene is determined in the promoter-proximal region. Genes Dev. 1992; 6:2201–2213. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

