eRNAbase: a comprehensive database for decoding the regulatory eRNAs in human and mouse
- PMID: 37889077
- PMCID: PMC10767853
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad925
eRNAbase: a comprehensive database for decoding the regulatory eRNAs in human and mouse
Abstract
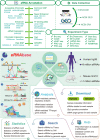
Enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) transcribed from distal active enhancers serve as key regulators in gene transcriptional regulation. The accumulation of eRNAs from multiple sequencing assays has led to an urgent need to comprehensively collect and process these data to illustrate the regulatory landscape of eRNAs. To address this need, we developed the eRNAbase (http://bio.liclab.net/eRNAbase/index.php) to store the massive available resources of human and mouse eRNAs and provide comprehensive annotation and analyses for eRNAs. The current version of eRNAbase cataloged 10 399 928 eRNAs from 1012 samples, including 858 human samples and 154 mouse samples. These eRNAs were first identified and uniformly processed from 14 eRNA-related experiment types manually collected from GEO/SRA and ENCODE. Importantly, the eRNAbase provides detailed and abundant (epi)genetic annotations in eRNA regions, such as super enhancers, enhancers, common single nucleotide polymorphisms, expression quantitative trait loci, transcription factor binding sites, CRISPR/Cas9 target sites, DNase I hypersensitivity sites, chromatin accessibility regions, methylation sites, chromatin interactions regions, topologically associating domains and RNA spatial interactions. Furthermore, the eRNAbase provides users with three novel analyses including eRNA-mediated pathway regulatory analysis, eRNA-based variation interpretation analysis and eRNA-mediated TF-target gene analysis. Hence, eRNAbase is a powerful platform to query, browse and visualize regulatory cues associated with eRNAs.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



References
-
- Li W., Notani D., Rosenfeld M.G.. Enhancers as non-coding RNA transcription units: recent insights and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016; 17:207–223. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 62171166/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20210002-1005 USCAT-2021-01/Affiliated Hospital of University of South China for Advanced Talents
- 2019M661311/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2023JJ30547/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 20201920/Scientific Research Fund Project of Hunan Provincial Health Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

