Landscape of Baseline and Acquired Genomic Alterations in Circulating Tumor DNA with Abemaciclib Alone or with Endocrine Therapy in Advanced Breast Cancer
- PMID: 37889120
- PMCID: PMC11094424
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3573
Landscape of Baseline and Acquired Genomic Alterations in Circulating Tumor DNA with Abemaciclib Alone or with Endocrine Therapy in Advanced Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To identify potential predictors of response and resistance mechanisms in patients with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), HER2-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer (ABC) treated with the cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor abemaciclib ± endocrine therapy (ET), baseline and acquired genomic alterations in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) were analyzed and associated with clinical outcomes.
Experimental design: MONARCH 3: postmenopausal women with HR+, HER2- ABC and no prior systemic therapy in the advanced setting were randomly assigned to abemaciclib or placebo plus nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI). nextMONARCH: women with HR+, HER2- metastatic breast cancer that progressed on/after prior ET and chemotherapy were randomly assigned to abemaciclib alone (two doses) or plus tamoxifen. Baseline and end-of-treatment plasma samples from patients in MONARCH 3 and nextMONARCH (monotherapy arms) were analyzed to identify somatic genomic alterations. Association between genomic alterations and median progression-free survival (mPFS) was assessed.
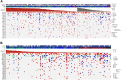
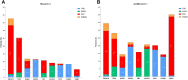
Results: Most patients had ≥1 genomic alteration detected in baseline ctDNA. In MONARCH 3, abemaciclib+NSAI was associated with improved mPFS versus placebo+NSAI, regardless of baseline alterations. ESR1 alterations were less frequently acquired in the abemaciclib+NSAI arm than placebo+NSAI. Acquired alterations potentially associated with resistance to abemaciclib ± NSAI included RB1 and MYC.
Conclusions: In MONARCH 3, certain baseline ctDNA genomic alterations were prognostic for ET but not predictive of abemaciclib response. Further studies are warranted to assess whether ctDNA alterations acquired during abemaciclib treatment differ from other CDK4/6 inhibitors. Findings are hypothesis generating; further exploration is warranted into mechanisms of resistance to abemaciclib and ET. See related commentary by Wander and Bardia, p. 2008.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures




References
-
- Eggersmann TK, Degenhardt T, Gluz O, Wuerstlein R, Harbeck N. CDK4/6 inhibitors expand the therapeutic options in breast cancer: palbociclib, ribociclib and abemaciclib. BioDrugs 2019;33:125–35. - PubMed
-
- Cristofanilli M, Turner NC, Bondarenko I, Ro J, Im S-A, Masuda N, et al. . Fulvestrant plus palbociclib versus fulvestrant plus placebo for treatment of hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer that progressed on previous endocrine therapy (PALOMA-3): final analysis of the multicentre, double-blind, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:425–39. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia SKL, Im S-A, Fasching PA, DeLaurentiis M, et al. . Ribociclib (RIB)+ fulvestrant (FUL) in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), HER2-negative (HER2–) advanced breast cancer (ABC): results from MONALEESA-3. J Clin Oncol 36:15s, 2018. (suppl; abstr 1000).
-
- Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J, Inoue K, Pivot X, et al. . MONARCH 2: abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer who had progressed while receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol 2017;35:2875–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

