KEAP1 mutation in lung adenocarcinoma promotes immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance
- PMID: 37889752
- PMCID: PMC10755970
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113295
KEAP1 mutation in lung adenocarcinoma promotes immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance
Abstract
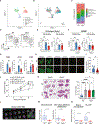
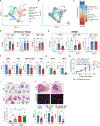
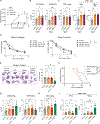
Lung cancer treatment has benefited greatly through advancements in immunotherapies. However, immunotherapy often fails in patients with specific mutations like KEAP1, which are frequently found in lung adenocarcinoma. We established an antigenic lung cancer model and used it to explore how Keap1 mutations remodel the tumor immune microenvironment. Using single-cell technology and depletion studies, we demonstrate that Keap1-mutant tumors diminish dendritic cell and T cell responses driving immunotherapy resistance. This observation was corroborated in patient samples. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated gene targeting revealed that hyperactivation of the NRF2 antioxidant pathway is responsible for diminished immune responses in Keap1-mutant tumors. Importantly, we demonstrate that combining glutaminase inhibition with immune checkpoint blockade can reverse immunosuppression, making Keap1-mutant tumors susceptible to immunotherapy. Our study provides new insight into the role of KEAP1 mutations in immune evasion, paving the way for novel immune-based therapeutic strategies for KEAP1-mutant cancers.
Keywords: CD103 DC; CP: Cancer; CP: Immunology; KEAP1; LUAD; NRF2; NSCLC; T cell; adenocarcinoma; immune surveillance; immunotherapy; lung cancer.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests T.P. has received research support from Agios Pharmaceuticals, and T.P. and S.B.K. have received funding from Dracen Pharmaceuticals, Kymera Therapeutics, and Bristol Myers Squibb. T.P. has received honoraria from Calithera Biosciences and Vividion Therapeutics. T.P. and S.B.K. are authors on US provisional patent application 16/483,835: “Methods for treating cancers having a deregulated NRF2/KEAP1 pathway.”
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA271245/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009161/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA229086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143861/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA252239/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI100853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA222504/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA247020/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007308/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA227649/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

