A community health worker-led program to improve access to gestational diabetes screening in urban slums of Pune, India: Results from a mixed methods study
- PMID: 37889879
- PMCID: PMC10610081
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0001622
A community health worker-led program to improve access to gestational diabetes screening in urban slums of Pune, India: Results from a mixed methods study
Abstract
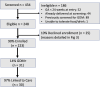
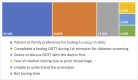
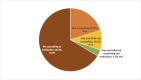
The World Health Organization recommends all pregnant women receive screening for gestational diabetes (GDM) with a fasting oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). However, very few women receive recommended screening in resource-limited countries like India. We implemented a community health worker (CHW)-delivered program to evaluate if home-based, CHW-delivered OGTT would increase GDM screening in a low-resource setting. We conducted a mixed methods study in two urban slum communities in Pune, India. CHWs were trained to deliver home-based, point-of-care fasting OGTT to women in their third trimester of pregnancy. The primary outcome was uptake of CHW-delivered OGTT. Secondary outcomes included GDM prevalence and linkage to GDM care. Individual interviews were conducted with purposively sampled pregnant women, CHWs, and local clinicians to assess barriers and facilitators of this approach. From October 2021-June 2022, 248 eligible pregnant women were identified. Of these, 223 (90%) accepted CHW-delivered OGTT and 31 (14%) were diagnosed with GDM. Thirty (97%) women diagnosed with GDM subsequently sought GDM care; only 10 (33%) received lifestyle counseling or pharmacologic therapy. Qualitative interviews indicated that CHW-delivered testing was considered highly acceptable as home-based testing saved time and was more convenient than clinic-based testing. Inconsistent clinical management of GDM was attributed to providers' lack of time to deliver counseling, and perceptions that low-income populations are not at risk for GDM. Convenience and trust in a CHW-delivered GDM screening program resulted in high access to gold-standard OGTT screening and identification of a high GDM prevalence among pregnant women in two urban slum communities. Appropriate linkage to care was limited by clinician time constraints and misperceptions of GDM risk. CHW-delivered GDM screening and counseling may improve health education and access to preventive healthcare, offloading busy public clinics in high-need, low-resource settings.
Copyright: © 2023 Chebrolu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Krishnaveni GV, Hill JC, Veena SR, Geetha S, Jayakumar MN, Karat CL, et al. Gestational diabetes and the incidence of diabetes in the 5 years following the index pregnancy in South Indian women. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;78(3):398–404. Epub 20070720. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2007.06.002 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colagiuri S, Falavigna M, Agarwal MM, Boulvain M, Coetzee E, Hod M, et al. Strategies for implementing the WHO diagnostic criteria and classification of hyperglycaemia first detected in pregnancy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;103(3):364–72. Epub 20140225. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.02.012 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nielsen KK, Rheinländer T, Kapur A, Damm P, Seshiah V, Bygbjerg IC. Factors influencing timely initiation and completion of gestational diabetes mellitus screening and diagnosis—a qualitative study from Tamil Nadu, India. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17(1):255. Epub 20170801. doi: 10.1186/s12884-017-1429-y . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
