Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Taro Leaf Antioxidants Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: An Eco-Friendly Strategy for the Valorization of Crop Residues
- PMID: 37891880
- PMCID: PMC10604219
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12101801
Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Taro Leaf Antioxidants Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: An Eco-Friendly Strategy for the Valorization of Crop Residues
Abstract
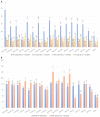
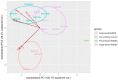
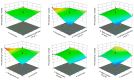
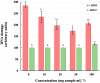
Colocasia esculenta L. leaves are considered a by-product of taro cultivation and are discarded as environmental waste, despite their valuable phenolic composition. Their valorization to obtain value-added substances for medicinal, food, and cosmetic applications is the aim of the current work. An ultrasound-assisted extraction was developed for the environmentally friendly and sustainable isolation of taro leaf antioxidants using natural deep eutectic solvents (NaDESs). Among the utilized solvents, the NaDES based on betaine and ethylene glycol provided the best extraction efficiencies in terms of polyphenolic content and antioxidant activity. Multi-response optimization suggested a solvent-to-solid ratio of 10 mL g-1, a processing time of 60 min, an extraction temperature of 60 °C, and a water content of 33.8% (w/w) as optimal extraction parameters. Leaf extract obtained under these optimum operational parameters demonstrated a strong radical scavenging activity against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (65.80 ± 0.87%), a high ferric reducing antioxidant power (126.62 ± 1.92 μmol TE g-1 sample), and significant protection against oxidative stress-induced DNA damage. The chromatographic characterization of the optimum extract revealed its richness in flavonoids (flavones and flavonols). The outcomes of the present study suggest that the proposed method could serve as a highly efficient and green alternative for the recovery of polyphenols from agricultural wastes.
Keywords: Colocasia esculenta L.; antioxidants; eco-friendly extraction; green chemistry; natural deep eutectic solvents (NaDESs); polyphenols; response surface methodology (RSM); taro leaves; ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE); waste valorization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Goncalves R.F., Silva A.M.S., Silva A.M., Valentao P., Ferreres F., Gil-Izquierdo A., Silva J.B., Santos D., Andrade P.B. Influence of Taro (Colocasia esculenta L. Shott) Growth Conditions on the Phenolic Composition and Biological Properties. Food Chem. 2013;141:3480–3485. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kumar V., Sharma H.K. Process Optimization for Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Taro (Colocasia esculenta), Using RSM and ANFIS Modeling. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017;11:704–718. doi: 10.1007/s11694-016-9440-y. - DOI
-
- Leong A.C.N., Kinjo Y., Tako M., Iwasaki H., Oku H., Tamaki H. Flavonoid Glycosides in the Shoot System of Okinawa Taumu (Colocasia esculenta S.) Food Chem. 2010;119:630–635. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.07.004. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

