Prediction of the Sleep Apnea Severity Using 2D-Convolutional Neural Networks and Respiratory Effort Signals
- PMID: 37892008
- PMCID: PMC10605440
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13203187
Prediction of the Sleep Apnea Severity Using 2D-Convolutional Neural Networks and Respiratory Effort Signals
Abstract
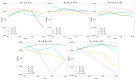
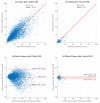
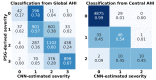
The high prevalence of sleep apnea and the limitations of polysomnography have prompted the investigation of strategies aimed at automated diagnosis using a restricted number of physiological measures. This study aimed to demonstrate that thoracic (THO) and abdominal (ABD) movement signals are useful for accurately estimating the severity of sleep apnea, even if central respiratory events are present. Thus, we developed 2D-convolutional neural networks (CNNs) jointly using THO and ABD to automatically estimate sleep apnea severity and evaluate the central event contribution. Our proposal achieved an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) = 0.75 and a root mean square error (RMSE) = 10.33 events/h when estimating the apnea-hypopnea index, and ICC = 0.83 and RMSE = 0.95 events/h when estimating the central apnea index. The CNN obtained accuracies of 94.98%, 79.82%, and 81.60% for 5, 15, and 30 events/h when evaluating the complete apnea hypopnea index. The model improved when the nature of the events was central: 98.72% and 99.74% accuracy for 5 and 15 events/h. Hence, the information extracted from these signals using CNNs could be a powerful tool to diagnose sleep apnea, especially in subjects with a high density of central apnea events.
Keywords: abdominal respiratory signal; central sleep apnea; convolutional neural network; deep learning; obstructive sleep apnea; thoracic respiratory signal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Berry R.B., Budhiraja R., Gottlieb D.J., Gozal D., Iber C., Kapur V.K., Marcus C.L., Mehra R., Parthasarathy S., Quan S.F., et al. Rules for Scoring Respiratory Events in Sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. Deliberations of the Sleep Apnea Definitions Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012;8:597. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.2172. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Epstein L.J., Kristo D., Strollo P.J., Friedman N., Malhotra A., Patil S.P., Ramar K., Rogers R., Schwab R.J., Weaver E.M., et al. Clinical Guideline for the Evaluation, Management and Long-term Care of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009;5:263. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.27497. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

