Synergistic Antimicrobial Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Redox-Active Nanoparticles
- PMID: 37893152
- PMCID: PMC10604215
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11102780
Synergistic Antimicrobial Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Redox-Active Nanoparticles
Abstract
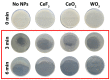
Cold argon plasma (CAP) and metal oxide nanoparticles are well known antimicrobial agents. In the current study, on an example of Escherichia coli, a series of analyses was performed to assess the antibacterial action of the combination of these agents and to evaluate the possibility of using cerium oxide and cerium fluoride nanoparticles for a combined treatment of bacterial diseases. The joint effect of the combination of cold argon plasma and several metal oxide and fluoride nanoparticles (CeO2, CeF3, WO3) was investigated on a model of E. coli colony growth on agar plates. The mutagenic effect of different CAP and nanoparticle combinations on bacterial DNA was investigated, by means of a blue-white colony assay and RAPD-PCR. The effect on cell wall damage, using atomic force microscopy, was also studied. The results obtained demonstrate that the combination of CAP and redox-active metal oxide nanoparticles (RAMON) effectively inhibits bacterial growth, providing a synergistic antimicrobial effect exceeding that of any of the agents alone. The combination of CAP and CeF3 was shown to be the most effective mutagen against plasmid DNA, and the combination of CAP and WO3 was the most effective against bacterial genomic DNA. The analysis of direct cell wall damage by atomic force microscopy showed the combination of CAP and CeF3 to be the most effective antimicrobial agent. The combination of CAP and redox-active metal oxide or metal fluoride nanoparticles has a strong synergistic antimicrobial effect on bacterial growth, resulting in plasmid and genomic DNA damage and cell wall damage. For the first time, a strong antimicrobial and DNA-damaging effect of CeF3 nanoparticles has been demonstrated.
Keywords: antimicrobial effect; bacteria; cerium fluoride; cerium oxide; cold argon plasma; combined treatment; nanoparticles; tungsten oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Laroussi M. Sterilization of contaminated matter with an atmospheric pressure plasma. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1996;24:1188–1191. doi: 10.1109/27.533129. - DOI
-
- Vatansever F., de Melo W.C., Avci P., Vecchio D., Sadasivam M., Gupta A., Chandran R., Karimi M., Parizotto N.A., Yin R., et al. Antimicrobial strategies centered around reactive oxygen species—Bactericidal antibiotics, photodynamic therapy, and beyond. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013;37:955–989. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

