Mental Health and Contraceptive Knowledge in High Schoolers: Comparing Remote and In-Person Learning during COVID-19
- PMID: 37893594
- PMCID: PMC10608468
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59101876
Mental Health and Contraceptive Knowledge in High Schoolers: Comparing Remote and In-Person Learning during COVID-19
Abstract
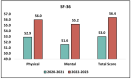
Background and Objectives: In response to the COVID-19 pandemic's effects on education, this study delves into the behavioral, mental health, and sexual education characteristics of high school students during 2020-2021 and 2022-2023. Materials and Methods: We evaluated a variety of factors, including substance use, academic performance, sexual activities, mental health support, pandemic-related anxiety levels, and quality of life indicators using standardized instruments such as the SF-36, GAD-7, and WHOQOL-BREF. Furthermore, we addressed specific questions concerning contraception and sexual education during this period. Results: The questionnaires were filled in by 44 students in 2020-2021 and 41 students in 2022-2023. Significant findings included a noteworthy increase in COVID-19 vaccination rates, from 18.2% in 2020-2021 to 39.0% in 2022-2023 (p = 0.033), enhanced perceptions of mental health support during remote learning, from 7.1% to 20.0% (p = 0.044), and a rise in students partaking in reproductive health discussions from 10.7% to 25.0% (p = 0.046). Additionally, there was a marked decline in anxiety regarding the transition back to in-person learning (p = 0.048). Health surveys, such as the SF-36, signaled improvements in both physical and mental health over the years (p = 0.046 and p = 0.019, respectively), while the GAD-7 scores depicted a considerable reduction in anxiety symptoms (p = 0.038). The WHOQOL-BREF results also highlighted a significant uptick in students' mental well-being in 2022-2023 (p = 0.039). Conclusions: As the COVID-19 pandemic ended, high school students exhibited shifts in behavior, health, and education over four academic years, particularly in areas of contraceptive knowledge and mental health outcomes. The pronounced enhancements in vaccination rates, perceptions of mental health support, participation in health conversations, and overall mental wellness emphasize the adaptability and resilience of students in these tumultuous periods, and a general increase in contraceptive knowledge and quality of life during the end of the pandemic.
Keywords: anxiety; contraception; depression; online education; teenagers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Contraception Awareness and Mental Well-Being in Teenagers and Young Adult Women: A Three-Year Cross-Sectional Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Nov 19;11(22):2990. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11222990. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998482 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving Mental Health Dynamics among Medical Students amid COVID-19: A Comparative Analysis of Stress, Depression, and Alcohol Use among Medical Students.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 18;59(10):1854. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101854. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893572 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental burden and quality of life in medical students - results of an online survey.GMS J Med Educ. 2023 Apr 17;40(2):Doc21. doi: 10.3205/zma001603. eCollection 2023. GMS J Med Educ. 2023. PMID: 37361244 Free PMC article.
-
Remote learning and mental health during the societal lockdown: a study of primary school students and parents in times of COVID-19.BMC Public Health. 2023 Jun 7;23(1):1106. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16040-9. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37286984 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among remote learning students during the COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from a meta-analysis.Front Psychol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1103925. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1103925. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36704682 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lowered hyoid bone overlapping the thyroid cartilage in CT angiograms.Surg Radiol Anat. 2024 Mar;46(3):333-339. doi: 10.1007/s00276-024-03300-5. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Surg Radiol Anat. 2024. PMID: 38315210
-
Status of Healthy Choices, Attitudes and Health Education of Children and Young People in Romania-A Literature Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Apr 27;60(5):725. doi: 10.3390/medicina60050725. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38792908 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nicolescu L.-C., Popescu C.-L., Popescu C.-V., Nicolescu C.-M., Nesiu A., Stanciu A.N., Mihu A.G. The evaluation of vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor in the case of patients with moderate COVID-19. Farmacia. 2022;70:507–513. doi: 10.31925/farmacia.2022.3.17. - DOI
-
- Toma A.-O., Prodan M., Reddyreddy A.R., Seclaman E., Crainiceanu Z., Bloanca V., Bratosin F., Dumitru C., Pilut C.N., Alambaram S., et al. The Epidemiology of Malignant Melanoma during the First Two Years of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022;20:305. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010305. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rossi I.V., de Lima J.D., Sabatke B., Nunes M.A.F., Ramirez G.E., Ramirez M.I. Active learning tools improve the learning outcomes, scientific attitude, and critical thinking in higher education: Experiences in an online course during the COVID-19 pandemic. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2021;49:888–903. doi: 10.1002/bmb.21574. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials