Eurotium cristatum from Fu Brick Tea Promotes Adipose Thermogenesis by Boosting Colonic Akkermansia muciniphila in High-Fat-Fed Obese Mice
- PMID: 37893609
- PMCID: PMC10606327
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12203716
Eurotium cristatum from Fu Brick Tea Promotes Adipose Thermogenesis by Boosting Colonic Akkermansia muciniphila in High-Fat-Fed Obese Mice
Abstract
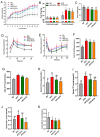
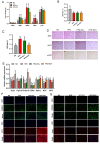
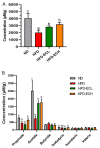
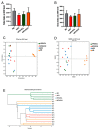
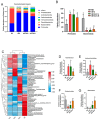
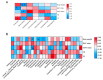
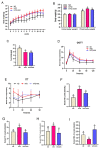
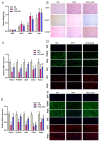
This study investigated the potential fat-thermogenic effects of Eurotium cristatum, and elucidated the underlying mechanisms. The 12-week administration of E. cristatum in HFD-fed obese mice reduced body weight and improved glucolipid metabolism disorders. The administration of E. cristatum also efficiently promoted thermogenesis by increasing the expression of UCP1 and PRDM16 in both interscapular brown adipose tissue (iBAT) and inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT) of HFD-fed mice. Furthermore, E. cristatum shaped the gut microbiome by increasing the abundance of Parabacteroides and Akkermansia muciniphila, and also elevated the levels of cecal short-chain fatty acids, particularly propionate and acetate. Of note, A. muciniphila was highly negatively correlated with body weight gain (r = -0.801, p < 0.05) and the iWAT index (r = -0.977, p < 0.01), suggesting that A. muciniphila may play an important role in the thermogenic mobilization induced by E. cristatum. Continuous supplementation with A. muciniphila suppressed adipose accumulation, improved glucolipid metabolism, and enhanced the thermogenic activity of iWAT and iBAT. Collectively, our results propose that boosted A. muciniphila acts as a key microbe in tea-derived probiotic E. cristatum-mediated fat-thermogenic and anti-obesity effects.
Keywords: Akkermansia muciniphila; Eurotium cristatum; Fu brick tea; fat thermogenesis; gut microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Xiao Y., He C., Chen Y., Huang Y., Gao Y., Hou A.Z., Li Y. UPLC-QQQ-MS/MS-based widely targeted metabolomic analysis reveals the effect of solid-state fermentation with Eurotium cristatum on the dynamic changes in the metabolite profile of dark tea. Food Chem. 2022;378:131999–132008. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131999. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang X.L., Liu X.X., Long B., Wei F.Y., Zhang J.P., Cui Y.X. Comparison of chemical constituents of Eurotium cristatum-mediated pure and mixed fermentation in summer-autumn tea. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021;143:111132. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111132. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 31871752/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32072175/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020ZDLSF01-07/key research and development plan in Shaanxi province
- 2022QFY09-06/key research and development plan in Shaanxi province
- GK202101006/Development Program for Innovative Research Team of Shaanxi Normal University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

