Inhibition of IEC-6 Cell Proliferation and the Mechanism of Ulcerative Colitis in C57BL/6 Mice by Dandelion Root Polysaccharides
- PMID: 37893693
- PMCID: PMC10606498
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12203800
Inhibition of IEC-6 Cell Proliferation and the Mechanism of Ulcerative Colitis in C57BL/6 Mice by Dandelion Root Polysaccharides
Abstract
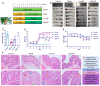
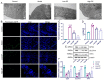
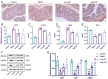
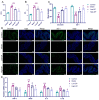
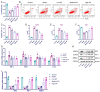
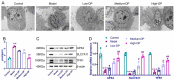
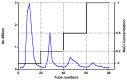
An exploration was conducted on the potential therapeutic properties of dandelion polysaccharide (DP) in addressing 3% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced ulcerative colitis (UC) in murine models. Subsequent assessments focused on DP's influence on inflammation, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis in IEC-6 cells damaged by H2O2. Results highlighted the efficacy of DP in mitigating weight loss, improving disease activity index scores, normalizing colon length, and alleviating histological abnormalities in the affected mice. DP repaired colonic mitochondrial damage by enhancing iron transport and inhibited iron death in colonic cells. Moreover, DP played a pivotal role in enhancing the antioxidant potential. This was evident from the increased expression levels of Nrf2, HO-1, NQO-1, and GSH, coupled with a decrease in MDA and 4-HNE markers in the UC-afflicted mice. Concurrently, DP manifested inhibitory effects on MPO activation and transcription levels of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and iNOS. An upsurge in the expression of occludin and ZO-1 was also observed. Restoration of intestinal tightness resulted in decreased serum LPS and LDH levels. Thereafter, administration of DP by gavage increased fecal flora diversity and relative abundance of probiotics in UC mice. Analysis of metabolites indicated that DP counteracted metabolic disturbances and augmented the levels of short-chain fatty acids in ulcerative colitis-affected mice. In vitro studies underscored the role of DP in triggering Nrf2 activation, which in turn exhibited anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-ferroptotic properties. Summarily, DP's capacity to activate Nrf2 contributes to the suppression of ferroptotic processes in intestinal epithelial cells of UC-affected mice, enhancing the intestinal barrier's integrity. Beyond that, DP possesses the ability to modulate the gut microbiome, rectify metabolic imbalances, rejuvenate short-chain fatty acid levels, and bolster the intestinal barrier as a therapeutic approach to UC.
Keywords: Nrf2; dandelion root polysaccharides; ferroptosis; gut flora; metabolites; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- You Y., Yoo S., Yoon H.G., Park J., Lee Y.H., Kim S., Oh K.T., Lee J., Cho H.Y., Jun W. In vitro and in vivo hepatoprotective effects of the aqueous extract from Taraxacum officinale (dandelion) root against alcohol-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010;48:1632–1637. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.03.037. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

