Chemical Composition, Functional and Anticancer Properties of Carrot
- PMID: 37894640
- PMCID: PMC10608851
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28207161
Chemical Composition, Functional and Anticancer Properties of Carrot
Abstract
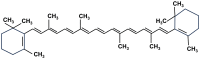
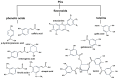
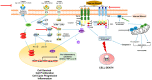
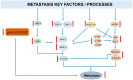
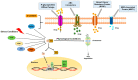
Plants are a valuable source of drugs for cancer treatment. Daucus carota has been investigated for its health properties. In particular, Daucus carota L. subsp. Sativus, the common edible carrot root, has been found to be rich in bioactive compounds such as carotenoids and dietary fiber and contains many other functional components with significant health-promoting features, while Daucus carota L. subsp. Carrot (Apiacae), also known as wild carrot, has been usually used for gastric ulcer therapy, diabetes, and muscle pain in Lebanon. Here, we review the chemical composition of Daucus carota L. and the functional properties of both edible and wild carrot subspecies. Then, we focus on compounds with anticancer characteristics identified in both Daucus carota subspecies, and we discuss their potential use in the development of novel anticancer therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Daucus carota L. phytochemicals; anti-metastatic compounds; anti-proliferative compounds; polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nguyen H.H.V. Handbook of Vegetables Preservation Processing. 2nd ed. Routledge; Abington, UK: 2015.
-
- Heywood V.H. Relationships and evolution in the Daucus carota complex. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 1983;32:51–65.
-
- Stolarczyk J., Janick J. Carrot: History and iconography. Chron. Hortic. 2011;51:2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

