The Effects of Probiotic Bacillus Spores on Dexamethasone-Treated Rats
- PMID: 37894792
- PMCID: PMC10606902
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242015111
The Effects of Probiotic Bacillus Spores on Dexamethasone-Treated Rats
Abstract
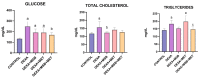
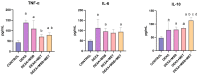
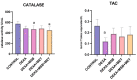
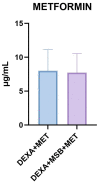
Glucocorticoids are effective anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents. Long-term exposure is associated with multiple metabolic side effects. Spore-forming probiotic bacteria have shown modulatory properties regarding glycolipid metabolism and inflammation. The aim of this study was to evaluate, for the first time, the effects of Bacillus species spores (B. licheniformis, B. indicus, B. subtilis, B. clausii, and B. coagulans) alone and in combination with metformin against dexamethasone-induced systemic disturbances. A total of 30 rats were randomly divided into 5 groups: group 1 served as control (CONTROL), group 2 received dexamethasone (DEXA), group 3 received DEXA and MegaSporeBiotic (MSB), group 4 received DEXA and metformin (MET), and group 5 received DEXA, MSB, and MET. On the last day of the experiment, blood samples and liver tissue samples for histopathological examination were collected. We determined serum glucose, total cholesterol, triglycerides, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-10 (IL-10), catalase, total antioxidant capacity (TAC), and metformin concentration. DEXA administration caused hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia, increased inflammation cytokines, and decreased antioxidant markers. Treatment with MSB reduced total cholesterol, suggesting that the administration of Bacillus spores-based probiotics to DEXA-treated rats could ameliorate metabolic parameters.
Keywords: Bacillus spores; dexamethasone; dyslipidemia; hyperglycemia; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study, in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
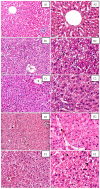
 ); large lipid droplets within the hepatocytes (
); large lipid droplets within the hepatocytes ( ); degenerated eosinophilic hepatocytes with pyknotic and hyperchromatic nuclei (
); degenerated eosinophilic hepatocytes with pyknotic and hyperchromatic nuclei ( ); loss of cellular borders; vascular congestion in the central vein (
); loss of cellular borders; vascular congestion in the central vein ( ); moderately dilated sinusoids with mild inflammatory infiltrate (polymorphonuclears neutrophils) within the sinusoids (
); moderately dilated sinusoids with mild inflammatory infiltrate (polymorphonuclears neutrophils) within the sinusoids ( ). (C): DEXA + MSB treated rat group; ((C1), 20×) and ((C2), 40×). Partial reduction in lipid accumulation with small perinuclear lipid droplets within the hepatocytes (
). (C): DEXA + MSB treated rat group; ((C1), 20×) and ((C2), 40×). Partial reduction in lipid accumulation with small perinuclear lipid droplets within the hepatocytes ( ); moderate improvement in hepatocytes structure; mild central vein ectasia (
); moderate improvement in hepatocytes structure; mild central vein ectasia ( ); sinusoidal stasis and dilatation with few inflammatory cells (
); sinusoidal stasis and dilatation with few inflammatory cells ( ). (D): DEXA + MET-treated rat group; ((D1), 20×); and ((D2), 40×). Important restoration of the hepatic architecture and hepatocyte structure, with a significant reduction of intra-hepatocyte lipid content (
). (D): DEXA + MET-treated rat group; ((D1), 20×); and ((D2), 40×). Important restoration of the hepatic architecture and hepatocyte structure, with a significant reduction of intra-hepatocyte lipid content ( ); congestion within the portal vessels (
); congestion within the portal vessels ( ) and sinusoids (
) and sinusoids ( ); mild central vein congestion and stasis (
); mild central vein congestion and stasis ( ). (E): DEXA + MSB + MET-treated rat group; ((E1), 20×); and ((E2), 40×). Poor improvement in hepatic lobular architecture and hepatocyte structure with still disorganized cords of cells and high intracellular lipid accumulation (intra-hepatocyte small (
). (E): DEXA + MSB + MET-treated rat group; ((E1), 20×); and ((E2), 40×). Poor improvement in hepatic lobular architecture and hepatocyte structure with still disorganized cords of cells and high intracellular lipid accumulation (intra-hepatocyte small ( ) and large lipid droplets) (
) and large lipid droplets) ( ); central vein congestion with intraluminal lymphocytes; (
); central vein congestion with intraluminal lymphocytes; ( ); moderate inflammatory infiltrate within the dilated sinusoids (
); moderate inflammatory infiltrate within the dilated sinusoids ( ). Abbreviations: H&E, hematoxylin, and eosin.
). Abbreviations: H&E, hematoxylin, and eosin.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

