Thrombin-Induced COX-2 Expression and PGE2 Synthesis in Human Tracheal Smooth Muscle Cells: Role of PKCδ/Pyk2-Dependent AP-1 Pathway Modulation
- PMID: 37894811
- PMCID: PMC10606820
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242015130
Thrombin-Induced COX-2 Expression and PGE2 Synthesis in Human Tracheal Smooth Muscle Cells: Role of PKCδ/Pyk2-Dependent AP-1 Pathway Modulation
Abstract
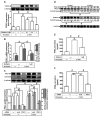
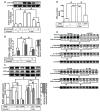
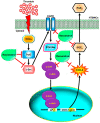
In this study, we confirmed that thrombin significantly increases the production of COX-2 and PGE2 in human tracheal smooth muscle cells (HTSMCs), leading to inflammation in the airways and lungs. These molecules are well-known contributors to various inflammatory diseases. Here, we investigated in detail the involved signaling pathways using specific inhibitors and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Our results demonstrated that inhibitors targeting proteins such as protein kinase C (PKC)δ, proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2), c-Src, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), or activator protein-1 (AP-1) effectively reduced thrombin-induced COX-2 and PGE2 production. Additionally, transfection with siRNAs against PKCδ, Pyk2, c-Src, EGFR, protein kinase B (Akt), or c-Jun mitigated these responses. Furthermore, our observations revealed that thrombin stimulated the phosphorylation of key components of the signaling cascade, including PKCδ, Pyk2, c-Src, EGFR, Akt, and c-Jun. Thrombin activated COX-2 promoter activity through AP-1 activation, a process that was disrupted by a point-mutated AP-1 site within the COX-2 promoter. Finally, resveratrol (one of the most researched natural polyphenols) was found to effectively inhibit thrombin-induced COX-2 expression and PGE2 release in HTSMCs through blocking the activation of Pyk2, c-Src, EGFR, Akt, and c-Jun. In summary, our findings demonstrate that thrombin-induced COX-2 and PGE2 generation involves a PKCδ/Pyk2/c-Src/EGFR/PI3K/Akt-dependent AP-1 activation pathway. This study also suggests the potential use of resveratrol as an intervention for managing airway inflammation.
Keywords: airway inflammation; cyclooxygenase; human tracheal smooth muscle cell; prostaglandin E2; resveratrol; thrombin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Kolmert J., Gómez C., Balgoma D., Sjödin M., Bood J., Konradsen J.R., Ericsson M., Thörngren J.O., James A., Mikus M., et al. Urinary Leukotriene E4 and Prostaglandin D2 metabolites increase in adult and childhood severe asthma characterized by type 2 inflammation. A clinical observational study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021;203:37–53. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201909-1869OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pucsok J.M., Györe I., Argay K., Huszár E., Barát E., Pucsok J., Horváth I. Effect of exercise on levels of cyclo-oxygenase mediators in exhaled breath condensate in elite athletes. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness. 2007;47:223–227. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

