Side-Chain Immune Oxysterols Induce Neuroinflammation by Activating Microglia
- PMID: 37894967
- PMCID: PMC10607006
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242015288
Side-Chain Immune Oxysterols Induce Neuroinflammation by Activating Microglia
Abstract
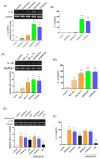
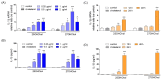
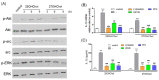
In individuals with Alzheimer's disease, the brain exhibits elevated levels of IL-1β and oxygenated cholesterol molecules (oxysterols). This study aimed to investigate the effects of side-chain oxysterols on IL-1β expression using HMC3 microglial cells and ApoE-deficient mice. Treatment of HMC3 cells with 25-hydroxycholesterol (25OHChol) and 27-hydroxycholesterol (27OHChol) led to increased IL-1β expression at the transcript and protein levels. Additionally, these oxysterols upregulated the surface expression of MHC II, a marker of activated microglia. Immunohistochemistry performed on the mice showed increased microglial expression of IL-1β and MHC II when fed a high-cholesterol diet. However, cholesterol and 24s-hydroxycholesterol did not increase IL-1β transcript levels or MHC II expression. The extent of IL-1β increase induced by 25OHChol and 27OHChol was comparable to that caused by oligomeric β-amyloid, and the IL-1β expression induced by the oxysterols was not impaired by polymyxin B, which inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-1β expression. Both oxysterols enhanced the phosphorylation of Akt, ERK, and Src, and inhibition of these kinase pathways with pharmacological inhibitors suppressed the expression of IL-1β and MHC II. The pharmacological agents chlorpromazine and cyclosporin A also impaired the oxysterol-induced expression of IL-1β and upregulation of MHC II. Overall, these findings suggest that dysregulated cholesterol metabolism leading to elevated levels of side-chain oxysterols, such as 25OHChol and 27OHChol, can activate microglia to secrete IL-1β through a mechanism amenable to pharmacologic intervention. The activation of microglia and subsequent neuroinflammation elicited by the immune oxysterols can contribute to the development of neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: immune oxysterol; interleukin-1β; microglia; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

