Taurine Protects Doxorubicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Its Membrane-Stabilizing Effect in Rats
- PMID: 37895413
- PMCID: PMC10608465
- DOI: 10.3390/life13102031
Taurine Protects Doxorubicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Its Membrane-Stabilizing Effect in Rats
Abstract
Background: Doxorubicin (dox) is a chemotherapeutic agent widely used against various tumors. However, the clinical use of this agent is limited due to various organ toxicities. Taurine is an intracellular free β-amino acid with antioxidant properties. The present study investigated the protective mechanism of taurine on dox-induced hepatotoxicity.
Methods: In total, 31 male Sprague-Dawley rats were used in the study. The control group received intraperitoneal (i.p.) 0.9% NaCl alone for 14 days; the taurine (Tau) group received i.p. taurine 150 mg/kg body weight/day for 14 days; the dox group received dox on days 12, 13, and 14 at a cumulative dose of 25 mg/kg body weight/3 days; and the tau+dox group received taurine and dox together at the same dose and through the same route. On day 15, biochemical evaluations were performed on blood samples taken from the left ventricle followed by histological examinations on liver samples.
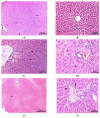
Results: Dox was found to increase liver function enzymes and tissue protein carbonyl levels, causing congestion and tissue damage, thereby leading to dysfunction. Tau was found to histologically preserve the liver morphology without showing any corrective effect on oxidative stress parameters. These findings suggest that the membrane-stabilizing effect of taurine may be more effective than its radical scavenging activity in preventing dox-induced toxicity.
Conclusion: Taurine can prevent doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity through non-antioxidant pathways.
Keywords: doxorubicin; hepatotoxicity; taurine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. All of the authors declare that they have participated in the design, execution, and analysis of the manuscript and that they have approved the final version.
Figures


References
-
- Shokrzadeh M., Bagheri A., Ghassemi-Barghi N., Rahmanian N., Eskandani M. Doxorubicin and doxorubicin-loaded nanoliposome induce senescence by enhancing oxidative stress, hepatotoxicity, and in vivo genotoxicity in male Wistar rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021;394:1803–1813. doi: 10.1007/s00210-021-02119-w. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

