Association between Perceived Psychological Stress and Exercise Behaviors: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the Survey of National Physical Fitness
- PMID: 37895440
- PMCID: PMC10608688
- DOI: 10.3390/life13102059
Association between Perceived Psychological Stress and Exercise Behaviors: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the Survey of National Physical Fitness
Abstract
Background: Perceived psychological stress and exercise are bidirectionally related, and the effects of exercise on stress relief are well documented. However, research on the influence of stress on exercise remains scarce. This study examined the association between perceived psychological stress and exercise participation among Korean adults and older adults as well as the relationship between exercise frequency and perceived stress.
Methods: Data on 3440 participants (2813 adults aged 19-64 and 627 older adults aged 65 or more) were collected from the Survey of National Physical Fitness conducted by the Korea Institute of Sport Science and the Korean Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism in 2015. We compared the participants' health-related behaviors, including exercise, regular breakfast consumption, and smoking, according to their perceived psychological stress levels.
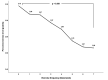
Results: Those who perceived a higher level of psychological stress reported lower levels of exercise participation, regular breakfast consumption, and smoking, with the exception of older male participants. The study also found that a higher frequency of exercise participation corresponded with a lower perceived level of psychological stress (β = -0.080, p < 0.001) and that engaging in physical activity even once a week yields a substantial reduction in stress levels.
Conclusions: In a large sample of Koreans, high levels of perceived psychological stress were significantly associated with less physical activity and infrequent weekly exercise. This study found a dose-response relationship between exercise frequency and reduced stress and suggested that psychological stress should be considered crucial in promoting physical activity.
Keywords: exercise; health behavior; physical activity; psychological stress; survey of national physical fitness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between Perceived Stress, Obesity, and Hypertension in Korean Adults and Older Adults.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;11(16):2271. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11162271. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628469 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Sports Club Participation, Physical Activity, and Health Behaviors Among Older Korean Adults.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Dec 1;12(23):2411. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12232411. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39685033 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of Breakfast Habits with Hypertension and Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study among Korean Adults and Older Adults.Iran J Public Health. 2025 Jan;54(1):175-185. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v54i1.17589. Iran J Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39902358 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Exercise Habits and Stress Among Individuals With Access to Internet-Connected Home Fitness Equipment: Single-Group Prospective Analysis.JMIR Form Res. 2023 Feb 8;7:e41877. doi: 10.2196/41877. JMIR Form Res. 2023. PMID: 36719817 Free PMC article.
-
American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Exercise and physical activity for older adults.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998 Jun;30(6):992-1008. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998. PMID: 9624662 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Moderate-Intensity Physical Exercise and Yoga Interventions on Stress in Hispanic College Students: A Pilot Study.Sports (Basel). 2025 Aug 13;13(8):266. doi: 10.3390/sports13080266. Sports (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40863775 Free PMC article.
-
The measured healthy lifestyle habits among Saudi university females in Medina, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 5;103(27):e38712. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038712. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38968502 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Frequency-Specific Microcurrent (FSM) Therapy and Relaxation in Adults with Distress: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 May 15;13(10):1151. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13101151. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427987 Free PMC article.
-
Maintaining exercise in fitness centre settings: insights from the physical activity maintenance theory.Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being. 2024 Dec;19(1):2409832. doi: 10.1080/17482631.2024.2409832. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being. 2024. PMID: 39359074 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Emotional Labor and Job Stress Perceived by Insurance and Asset Managers on Their Job Satisfaction.Iran J Public Health. 2024 May;53(5):1096-1103. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v53i5.15591. Iran J Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38912136 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources