Quantum Honeypots
- PMID: 37895582
- PMCID: PMC10606432
- DOI: 10.3390/e25101461
Quantum Honeypots
Abstract
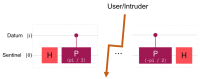
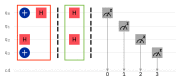
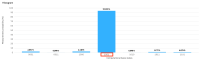
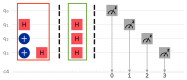
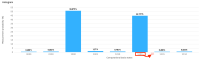
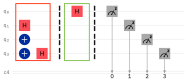
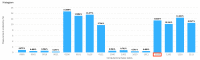
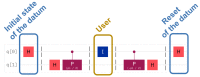
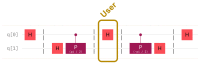
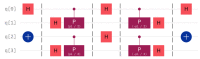
Quantum computation offers unique properties that cannot be paralleled by conventional computers. In particular, reading qubits may change their state and thus signal the presence of an intruder. This paper develops a proof-of-concept for a quantum honeypot that allows the detection of intruders on reading. The idea is to place quantum sentinels within all resources offered within the honeypot. Additional to classical honeypots, honeypots with quantum sentinels can trace the reading activity of the intruder within any resource. Sentinels can be set to be either visible and accessible to the intruder or hidden and unknown to intruders. Catching the intruder using quantum sentinels has a low theoretical probability per sentinel, but the probability can be increased arbitrarily higher by adding more sentinels. The main contributions of this paper are that the monitoring of the intruder can be carried out at the level of the information unit, such as the bit, and quantum monitoring activity is fully hidden from the intruder. Practical experiments, as performed in this research, show that the error rate of quantum computers has to be considerably reduced before implementations of this concept are feasible.
Keywords: honeypot; post-quantum security; quantum networks; quantum security.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fan W., Du Z., Fernández D., Villagra V. Enabling an Anatomic View to Investigate Honeypot Systems: A Survey. IEEE Syst. J. 2017;12:3906–3919. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2017.2762161. - DOI
-
- Spitzner L. Honeypots: Tracking Hackers. Addison-Wesley; Boston, MA, USA: 2002.
-
- Nielsen M., Chuang I. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2000.
-
- Grover L. A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search; Proceedings of the 28th Annual ACM Symposium on the Theory of Computing; Philadelphia, PA, USA. 22–24 May 1996; pp. 212–220.
-
- Shor P.W. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. Spec. Issue Quantum Comput. SIAM J. Comput. 1997;26:1484–1509. doi: 10.1137/S0097539795293172. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

