Morroniside Inhibits Inflammatory Bone Loss through the TRAF6-Mediated NF-κB/MAPK Signalling Pathway
- PMID: 37895909
- PMCID: PMC10609728
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16101438
Morroniside Inhibits Inflammatory Bone Loss through the TRAF6-Mediated NF-κB/MAPK Signalling Pathway
Abstract
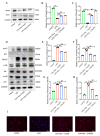
Osteoporosis is a chronic inflammatory disease that severely affects quality of life. Cornus officinalis is a Chinese herbal medicine with various bioactive ingredients, among which morroniside is its signature ingredient. Although anti-bone resorption drugs are the main treatment for bone loss, promoting bone anabolism is more suitable for increasing bone mass. Therefore, identifying changes in bone formation induced by morroniside may be conducive to developing effective intervention methods. In this study, morroniside was found to promote the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) and inhibit inflammation-induced bone loss in an in vivo mouse model of inflammatory bone loss. Morroniside enhanced bone density and bone microstructure, and inhibited the expression of IL6, IL1β, and ALP in serum (p < 0.05). Furthermore, in in vitro experiments, BMSCs exposed to 0-256 μM morroniside did not show cytotoxicity. Morroniside inhibited the expression of IL6 and IL1β and promoted the expression of the osteogenic transcription factors Runx2 and OCN. Furthermore, morroniside promoted osteocalcin and Runx2 expression and inhibited TRAF6-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling, as well as osteoblast growth and NF-κB nuclear transposition. Thus, morroniside promoted osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs, slowed the occurrence of the inflammatory response, and inhibited bone loss in mice with inflammatory bone loss.
Keywords: TRAF6-mediated MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway; inflammation; morroniside; osteogenic differentiation; osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Song H., Li B., Guo R., He S., Peng Z., Qu J., Zhao Y., Zhai X., Yin W., Yang K., et al. Hypoxic preconditioned aged BMSCs accelerates MI injury repair by modulating inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022;627:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Redlich K., Smolen J.S. Inflammatory bone loss: Pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012;11:234–250. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

