Improving Drug Delivery on Candida Albicans Using Geraniol Nanoemulsion
- PMID: 37896235
- PMCID: PMC10609964
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102475
Improving Drug Delivery on Candida Albicans Using Geraniol Nanoemulsion
Abstract
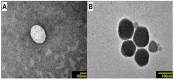
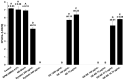
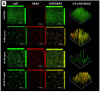
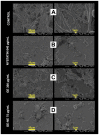
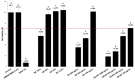
Geraniol (GE) is a monoterpene alcohol with excellent antifungal activity. However, its low solubility and high volatility impair its use. Nanoemulsions (NE) are excellent delivery systems for poorly soluble and volatile drugs, achieving controlled release of the active ingredient. The aim of this study was to improve the delivery of geraniol (GE) incorporated in NE against Candida albicans in order to evaluate the antibiofilm effect and cytotoxicity. Nanoemulsion containing 10% oil phase (cholesterol) (w/w), 10% surfactant (mixture of soy phosphatidylcholine and Brij 58; 1:2) (w/w), and 80% aqueous phase (phosphate buffer) (w/w) was synthesized. Incorporation of GE was carried out by sonication and the final compounds were characterized by hydrodynamic diameter, polydispersity index (PDI), and zeta potential (ZP), in addition to evaluation of physicochemical stability after 6 months and 1 year. The GE-NE effect was evaluated on Candida albicans biofilms and cytotoxic effect was evaluated on immortalized normal oral cell line NOK-Si. The diameter of GE-NE was 232.3 ± 2.7 nm and PDI 0.155 with exhibited homogeneity and stability in solution. GE-NE showed antibiofilm activity at a concentration of 75 μg/mL with reduction of >6.0 log10, and no cytotoxicity against NOK-Si cells at concentrations below 150 μg/mL was observed. GE-NE proved to be a promising candidate for prevention and treatment of fungal diseases.
Keywords: C. albicans; antifungal; biofilm; citotoxity; geraniol; nanoemulsion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anti-Candida auris activity in vitro and in vivo of micafungin loaded nanoemulsions.Med Mycol. 2023 Feb 3;61(2):myac090. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myac090. Med Mycol. 2023. PMID: 36427066
-
Preparation and Evaluation of Nanoemulsion of Citronella Essential Oil with Improved Antimicrobial and Anti-Cancer Properties.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Feb 27;12(3):478. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030478. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978345 Free PMC article.
-
Syngonanthus nitens (Bong.) Ruhland Derivatives Loaded into a Lipid Nanoemulsion for Enhanced Antifungal Activity Against Candida parapsilosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(14):1556-1565. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200317131041. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32183660
-
Formulation and optimization of nanoemulsion using antifungal lipid and surfactant for accentuated topical delivery of Amphotericin B.Drug Deliv. 2016 Oct;23(8):3101-3110. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2016.1153747. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 27854145
-
Role of architecture of N-oxide surfactants in the design of nanoemulsions for Candida skin infection.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020 Mar;187:110639. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110639. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020. PMID: 31776055
Cited by
-
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of Geraniol: an alternative perspective for metabolic disease management.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Dec;32(6):3653-3668. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01582-0. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39460887 Review.
References
-
- Francisconi R.S., Maquera-Huacho P.M., Tonon C.C., Calixto G.M.F., de Cássia Orlandi Sardi J., Chorilli M., Spolidorio D.M.P. Terpinen-4-ol and nystatin co-loaded precursor of liquid crystalline system for topical treatment of oral candidiasis. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:12984. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70085-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

