Recent Advancements in Development and Therapeutic Applications of Genome-Targeting Triplex-Forming Oligonucleotides and Peptide Nucleic Acids
- PMID: 37896275
- PMCID: PMC10609763
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102515
Recent Advancements in Development and Therapeutic Applications of Genome-Targeting Triplex-Forming Oligonucleotides and Peptide Nucleic Acids
Abstract
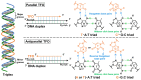
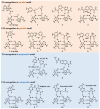
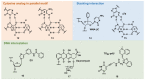
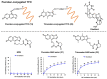
Recent developments in artificial nucleic acid and drug delivery systems present possibilities for the symbiotic engineering of therapeutic oligonucleotides, such as antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and small interfering ribonucleic acids (siRNAs). Employing these technologies, triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) or peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) can be applied to the development of symbiotic genome-targeting tools as well as a new class of oligonucleotide drugs, which offer conceptual advantages over antisense as the antigene target generally comprises two gene copies per cell rather than multiple copies of mRNA that are being continually transcribed. Further, genome editing by TFOs or PNAs induces permanent changes in the pathological genes, thus facilitating the complete cure of diseases. Nuclease-based gene-editing tools, such as zinc fingers, CRISPR-Cas9, and TALENs, are being explored for therapeutic applications, although their potential off-target, cytotoxic, and/or immunogenic effects may hinder their in vivo applications. Therefore, this review is aimed at describing the ongoing progress in TFO and PNA technologies, which can be symbiotic genome-targeting tools that will cause a near-future paradigm shift in drug development.
Keywords: antigene; genome editing; oligonucleotide therapeutic; peptide nucleic acid; triplex-forming oligonucleotide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Debugging the genetic code: non-viral in vivo delivery of therapeutic genome editing technologies.Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018 Sep;7:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018. PMID: 30984891 Free PMC article.
-
Triplex-mediated genome targeting and editing.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1114:115-42. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-761-7_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24557900
-
Development and Crosslinking Properties of Psoralen-Conjugated Triplex-Forming Oligonucleotides as Antigene Tools Targeting Genome DNA.ChemMedChem. 2023 Nov 2;18(21):e202300348. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202300348. Epub 2023 Sep 28. ChemMedChem. 2023. PMID: 37704578
-
Peptide nucleic acids: Advanced tools for biomedical applications.J Biotechnol. 2017 Oct 10;259:148-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.07.026. Epub 2017 Jul 29. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28764969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress of Triplex DNA Formation and Its Applications.J Med Chem. 2025 Mar 13;68(5):5055-5074. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02518. Epub 2025 Feb 28. J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40019113 Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition of mismatched sites in double-stranded DNA by a pair of partially noncomplementary peptide nucleic acids.Chem Lett. 2024 Dec 10;53(12):upae234. doi: 10.1093/chemle/upae234. eCollection 2024 Dec. Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 39677325 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of mixed-sequence double-stranded DNA regions using chimeric Invader/LNA probes.Org Biomol Chem. 2025 Jan 15;23(3):619-628. doi: 10.1039/d4ob01403k. Org Biomol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39412680 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive study of Z-DNA density and its evolutionary implications in birds.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 21;25(1):1123. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11039-x. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39573987 Free PMC article.
-
A third strand for protein-DNA interactions.Nat Chem. 2024 Nov;16(11):1748-1750. doi: 10.1038/s41557-024-01652-4. Nat Chem. 2024. PMID: 39406977 Free PMC article.
-
Development and functional evaluation of a psoralen-conjugated nucleoside mimic for triplex-forming oligonucleotides.Commun Chem. 2025 Jan 22;8(1):18. doi: 10.1038/s42004-025-01416-2. Commun Chem. 2025. PMID: 39843926 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

