Study of Damage Prediction of Carbon Fiber Tows Using Eddy Current Measurement
- PMID: 37896426
- PMCID: PMC10610890
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15204182
Study of Damage Prediction of Carbon Fiber Tows Using Eddy Current Measurement
Abstract
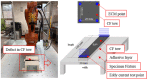
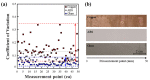
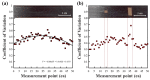
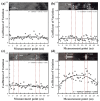
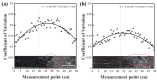
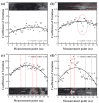
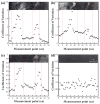
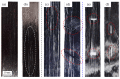
When manufacturing fiber-reinforced composites, it is possible to improve the quality of fiber steel fire and reduce the number of cracks in the finished product if it is possible to quickly identify the defects of the fiber tow. Therefore, in this study, we developed a method to identify the condition of carbon fiber tow using eddy current test (ECT), which is used to improve the quality of composite materials. Using the eddy current detection sensor, we checked the impedance results according to the condition of the CF tow. We found that the materials of the workbench used in the experiment greatly affected the ECT results, so it is necessary to use a material with a non-conductive and smooth surface. We evaluated the impedance results of the carbon fiber at 2 mm intervals using the ECT sensor and summarized the impedance results according to the fiber width direction, presenting the condition of the section as a constant of variation (CV). If the condition of the carbon fiber tow was unstable, the deviation of the CV per section was large. In particular, the deviation of the CV per section was more than 0.15 when the arrangement of the fibers was changed, foreign substances were formed on the surface of the fibers, and damage occurred in the direction of the fiber width of more than 4 mm, so it was easy to evaluate the quality on CF tow.
Keywords: Eddy current testing; carbon fiber; damage detection; evaluation; impedance.
Conflict of interest statement
Jae Chung Ha was employed by the company Vastek Korea. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Albakri M.I., Sturm L.D., Williams C.B., Tarazaga P.A. Impedance-based non-destructive evaluation of additively manufactured parts. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2017;23:589–601. doi: 10.1108/RPJ-03-2016-0046. - DOI
-
- Mayr G., Plank B., Sekelja J., Hendorfer G. Active thermography as a quantitative method for non-destructive evaluation of porous carbon fiber reinforced polymers. NDT E Int. 2011;44:537–543. doi: 10.1016/j.ndteint.2011.05.012. - DOI
-
- Dwivedi S.K., Vishwakarma M., Soni A. Advances and researches on non destructive testing: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2018;5:3690–3698. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2017.11.620. - DOI
-
- Yehia S., Abudayyeh O., Nabulsi S., Abdelqader I. Detection of common defects in concrete bridge decks using nondestructive evaluation techniques. J. Bridge Eng. 2007;12:215–225. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2007)12:2(215). - DOI
Grants and funding
- RS-2021-KA162366/the Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement
- 2020R1A6A03038697/Ministry of Education
- P0017310/Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE)
- G2820220600004/Korea Carbon Industry Promotion Agency funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy of the Republic of Korea
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

