Enhanced and Proficient Soft Template Array of Polyaniline-TiO2 Nanocomposites Fibers Prepared Using Anionic Surfactant for Fuel Cell Hydrogen Storage
- PMID: 37896429
- PMCID: PMC10610601
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15204186
Enhanced and Proficient Soft Template Array of Polyaniline-TiO2 Nanocomposites Fibers Prepared Using Anionic Surfactant for Fuel Cell Hydrogen Storage
Abstract
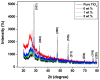
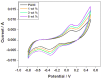
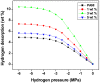
Porous TiO2-doped polyaniline and polyaniline nanocomposite fibers prepared by the in situ polymerization technique using anionic surfactant in an ice bath were studied. The prepared nanocomposites were characterized by FTIR spectroscopy and XRD patterns for structural analysis. The surface morphology of the polyaniline and its nanocomposites was examined using SEM images. DC conductivity shows the three levels of conductivity inherent in a semiconductor. Among the nanocomposites, the maximum DC conductivity is 5.6 S/cm for 3 wt.% polyaniline-TiO2 nanocomposite. Cyclic voltammetry shows the properties of PANI due to the redox peaks of 0.93 V and 0.24 V. Both peaks are due to the redox transition of PANI from the semiconductor to the conductive state. The hydrogen absorption capacity is approximately 4.5 wt.%, but at 60 °C the capacity doubles to approximately 7.3 wt.%. Conversely, 3 wt.% PANI-TiO2 nanocomposites have a high absorption capacity of 10.4 wt.% compared to other nanocomposites. An overall desorption capacity of 10.4 wt.% reduced to 96% was found for 3 wt.% TiO2-doped PANI nanocomposites.
Keywords: DC conductivity; hydrogen storage; nanocomposites; polyaniline fiber; surfactant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Chen Y., Zhu H., Liu Y. Preparation of activated rectangular polyaniline-based carbon tubes and their application in hydrogen adsorption. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2011;36:11738–11745. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.01.119. - DOI
-
- Lenin R., Singh A., Bera C. Effect of dopants and morphology on the electrical properties of polyaniline for various applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021;32:24710–24725. doi: 10.1007/s10854-021-06883-6. - DOI
-
- Kamarudin S., Asmal Rani M.S., Mohammad M., Mohammed N.H., Su’ait M.S., Ibrahim M.A., Asim N., Razali H. Investigation on size and conductivity of polyaniline nanofiber synthesised by surfactant-free polymerization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021;14:255–261. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.06.057. - DOI
-
- Cho S.J., Choo K., Kim D.P., Kim J.W. H2 sorption in HCl-treated polyaniline and polypyrrole. Catal. Today. 2007;120:336–340. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2006.09.007. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

