Rapid Method of Wastewater Classification by Electronic Nose for Performance Evaluation of Bioreactors with Activated Sludge
- PMID: 37896672
- PMCID: PMC10610685
- DOI: 10.3390/s23208578
Rapid Method of Wastewater Classification by Electronic Nose for Performance Evaluation of Bioreactors with Activated Sludge
Abstract
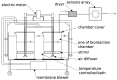
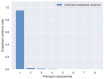
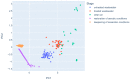
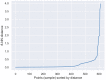
Currently, e-noses are used for measuring odorous compounds at wastewater treatment plants. These devices mimic the mammalian olfactory sense, comprising an array of multiple non-specific gas sensors. An array of sensors creates a unique set of signals called a "gas fingerprint", which enables it to differentiate between the analyzed samples of gas mixtures. However, appropriate advanced analyses of multidimensional data need to be conducted for this purpose. The failures of the wastewater treatment process are directly connected to the odor nuisance of bioreactors and are reflected in the level of pollution indicators. Thus, it can be assumed that using the appropriately selected methods of data analysis from a gas sensors array, it will be possible to distinguish and classify the operating states of bioreactors (i.e., phases of normal operation), as well as the occurrence of malfunction. This work focuses on developing a complete protocol for analyzing and interpreting multidimensional data from a gas sensor array measuring the properties of the air headspace in a bioreactor. These methods include dimensionality reduction and visualization in two-dimensional space using the principal component analysis (PCA) method, application of data clustering using an unsupervised method by Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) algorithm, and at the last stage, application of extra trees as a supervised machine learning method to achieve the best possible accuracy and precision in data classification.
Keywords: DBSCAN algorithm; activated sludge; electronic nose; extra trees; multidimensional data analysis; performance evaluation; principal component analysis; wastewater classification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aghdam E., Mohandes S.R., Manu P., Cheung C., Yunusa-Kaltungo A., Zayed T. Predicting Quality Parameters of Wastewater Treatment Plants Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2023;405:137019. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137019. - DOI
-
- Henze M., van Loosdrecht M.C.M., Ekama G.A., Brdjanovic D. Biological Wastewater Treatment: Principles, Modelling and Design. IWA Publishing; London, UK: 2008.
-
- Łagód G., Drewnowski J., Guz Ł., Piotrowicz A., Suchorab Z., Drewnowska M., Jaromin-Gleń K., Szeląg B. Rapid On-Line Method of Wastewater Parameters Estimation by Electronic Nose for Control and Operating Wastewater Treatment Plants toward Green Deal Implementation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022;275:56–68. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2022.28638. - DOI
-
- Corominas L., Garrido-Baserba M., Villez K., Olsson G., Cortés U., Poch M. Transforming Data into Knowledge for Improved Wastewater Treatment Operation: A Critical Review of Techniques. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018;106:89–103. doi: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.11.023. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

