Entropy-Based Machine Learning Model for Fast Diagnosis and Monitoring of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 37896703
- PMCID: PMC10610702
- DOI: 10.3390/s23208609
Entropy-Based Machine Learning Model for Fast Diagnosis and Monitoring of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
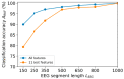
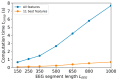
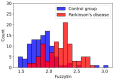
This study presents the concept of a computationally efficient machine learning (ML) model for diagnosing and monitoring Parkinson's disease (PD) using rest-state EEG signals (rs-EEG) from 20 PD subjects and 20 normal control (NC) subjects at a sampling rate of 128 Hz. Based on the comparative analysis of the effectiveness of entropy calculation methods, fuzzy entropy showed the best results in diagnosing and monitoring PD using rs-EEG, with classification accuracy (ARKF) of ~99.9%. The most important frequency range of rs-EEG for PD-based diagnostics lies in the range of 0-4 Hz, and the most informative signals were mainly received from the right hemisphere of the head. It was also found that ARKF significantly decreased as the length of rs-EEG segments decreased from 1000 to 150 samples. Using a procedure for selecting the most informative features, it was possible to reduce the computational costs of classification by 11 times, while maintaining an ARKF ~99.9%. The proposed method can be used in the healthcare internet of things (H-IoT), where low-performance edge devices can implement ML sensors to enhance human resilience to PD.
Keywords: EEG; Parkinson’s disease; diagnosis; edge device; entropy; human resilience; machine learning; monitoring; smart IoT environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization Aging and Health. [(accessed on 1 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health.
-
- Gomez C., Chessa S., Fleury A., Roussos G., Preuveneers D. Internet of Things for enabling smart environments: A technology-centric perspective. J. Ambient Intell. Smart Environ. 2019;11:23–43. doi: 10.3233/AIS-180509. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

