Long COVID Prevalence and the Impact of the Third SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dose: A Cross-Sectional Analysis from the Third Follow-Up of the Borriana Cohort, Valencia, Spain (2020-2022)
- PMID: 37896992
- PMCID: PMC10611325
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11101590
Long COVID Prevalence and the Impact of the Third SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dose: A Cross-Sectional Analysis from the Third Follow-Up of the Borriana Cohort, Valencia, Spain (2020-2022)
Abstract
Background: In March 2020, a COVID-19 outbreak linked to mass gathering dinners at the Falles Festival in Borriana, Spain, resulted in an estimated attack rate of 42.6% among attendees.
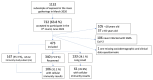
Methods: In June 2022, we conducted a cross-sectional follow-up study of 473 adults aged 18 to 64 who attended the dinners at the Falles Festival in 2020, examining the cumulative experience after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination responses. Data included demographic details, lifestyle habits, medical history, infection records, and vaccinations from a population-based vaccine registry. Blood samples were analyzed for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and cellular immunity. We employed a doubly robust inverse-probability weighting analysis to estimate the booster vaccine dose's impact on long COVID prevalence and symptom count.
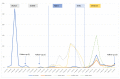
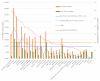
Results: A total of 28.1% of participants met the WHO criteria for long COVID, with older individuals showing higher rates. Long COVID diagnosis was less likely with factors including O blood group, higher occupational status, physical activity, three vaccine doses, strong SARS-CoV-2-S-reactive IFNγ-producing-CD8+ response, and infection during the Omicron period. Increased age, high or low social activity, underlying health conditions, a severe initial COVID episode, and reinfection were associated with higher long COVID likelihood. A booster dose, compared to one or two doses, reduced long COVID risk by 74% (95% CI: 56% to 92%) and symptom count by 55% (95% CI: 32% to 79%).
Conclusion: Long COVID was prevalent in a significant portion of those who contracted COVID-19, underscoring the need for sustained follow-up and therapeutic strategies. Vaccinations, notably the booster dose, had a substantial beneficial effect on long-term infection outcomes, affirming the vaccination's role in mitigating SARS-CoV-2 infection consequences.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 vaccination; booster dose; cellular immunity; human; long COVID; prevalence; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2023. Dashboard WHE.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

