In Vitro Transcribed RNA-Based Platform Vaccines: Past, Present, and Future
- PMID: 37897003
- PMCID: PMC10610676
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11101600
In Vitro Transcribed RNA-Based Platform Vaccines: Past, Present, and Future
Abstract
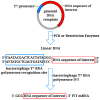
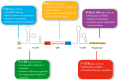
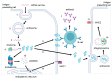
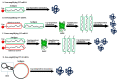
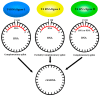
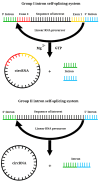
mRNA was discovered in 1961, but it was not used as a vaccine until after three decades. Recently, the development of mRNA vaccine technology gained great impetus from the pursuit of vaccines against COVID-19. To improve the properties of RNA vaccines, and primarily their circulation time, self-amplifying mRNA and trans-amplifying mRNA were developed. A separate branch of mRNA technology is circular RNA vaccines, which were developed with the discovery of the possibility of translation on their protein matrix. Circular RNA has several advantages over mRNA vaccines and is considered a fairly promising platform, as is trans-amplifying mRNA. This review presents an overview of the mRNA platform and a critical discussion of the more modern self-amplifying mRNA, trans-amplifying mRNA, and circular RNA platforms created on its basis. Finally, the main features, advantages, and disadvantages of each of the presented mRNA platforms are discussed. This discussion will facilitate the decision-making process in selecting the most appropriate platform for creating RNA vaccines against cancer or viral diseases.
Keywords: circular RNA vaccine; immunogenicity; mRNA vaccine; self-amplifying mRNA vaccine; trans-amplifying mRNA vaccine; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Importance of RNA-Based Vaccines in the Fight against COVID-19: An Overview.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Nov 17;9(11):1345. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9111345. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trans-Amplifying RNA: A Journey from Alphavirus Research to Future Vaccines.Viruses. 2024 Mar 25;16(4):503. doi: 10.3390/v16040503. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trans-Amplifying RNA Vaccines Against Infectious Diseases: A Comparison with Non-Replicating and Self-Amplifying RNA.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2786:135-144. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3770-8_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38814392
-
mRNA vaccines: Past, present, future.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022 Jul;17(4):491-522. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2022.05.003. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 36105317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogenicity and safety of a booster dose of a self-amplifying RNA COVID-19 vaccine (ARCT-154) versus BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: a double-blind, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2024 Apr;24(4):351-360. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00650-3. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38141632 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The inorganic pyrophosphatases of microorganisms: a structural and functional review.PeerJ. 2024 Jun 24;12:e17496. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17496. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38938619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mRNA cancer vaccines from bench to bedside: a new era in cancer immunotherapy.Biomark Res. 2024 Dec 18;12(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00692-9. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39696625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the advances of non-coding RNAs on the tumor microenvironment: innovative strategies for cancer therapies.J Transl Med. 2025 Jun 2;23(1):614. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06629-6. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40457447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolutionizing immunization: a comprehensive review of mRNA vaccine technology and applications.Virol J. 2025 Mar 12;22(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02645-6. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40075519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mRNA vaccines in tumor targeted therapy: mechanism, clinical application, and development trends.Biomark Res. 2024 Aug 31;12(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00644-3. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39217377 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

