Efficacy of non-conventional synthetic DMARDs for patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37899093
- PMCID: PMC10619071
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003487
Efficacy of non-conventional synthetic DMARDs for patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the efficacy of non-conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (ncs-DMARD) strategies on patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)-associated interstitial lung disease (ILD).
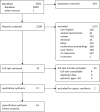
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library and Web of Science were searched for relevant articles from inception to 1 June 2022. The results obtained from the analysis were expressed as mean difference (MD), effect size and 95% CI.
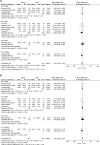
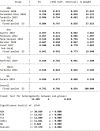
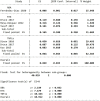
Results: A total of 17 studies, including 1315 patients with RA-ILD, were eligible. The ncs-DMARDs included abatacept, rituximab, tocilizumab, tumour necrosis factor and Janus kinase inhibitors. Compared with the baseline, there were no significant changes in forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1) and diffusion lung capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) values in the pooled data after ncs-DMARD treatment (alone or combined with conventional therapy) (p=0.36 for FVC; p=0.96 for FEV1 and p=0.46 for DLCO). Of note, FVC was obviously increased in rituximab subgroup (MD=-4.62, 95% CI -8.90 to -0.33, p=0.03). Also, high-resolution CT non-progression rate and fatality rate due to ILD progression in patients with RA-ILD were 0.792 (95% CI 0.746 to 0.834, p=0.015) and 0.049 (95% CI 0.035 to 0.065, p=0.000), respectively.
Conclusion: ncs-DMARDs alone or combined with conventional therapy might be an optimal and promising treatment for stabilising or improving ILD in patients with RA-ILD.
Prospero registration number: CRD42022356816.
Keywords: Antirheumatic Agents; Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Biological Therapy; Pulmonary Fibrosis; Qualitative research.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
