HLA-DPA1 overexpression inhibits cancer progression, reduces resistance to cisplatin, and correlates with increased immune infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 37899135
- PMCID: PMC10637812
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205082
HLA-DPA1 overexpression inhibits cancer progression, reduces resistance to cisplatin, and correlates with increased immune infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Human Leukocyte Antigen-DP alpha 1 (HLA-DPA1) is a critical gene in antigen-presenting cells and plays a significant role in immune regulation. The objective of this study was to comprehensively analyze the roles of HLA-DPA1 and its association with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Methods: We utilized bioinformatics and conducted a meta-analysis to examine the roles of HLA-DPA1 expression on the progression and immunity of LUAD. We also performed CCK-8, wound healing, and Transwell assays to validate the functions of HLA-DPA1 in LUAD.
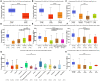
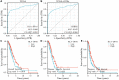
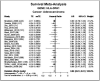
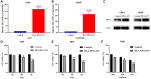
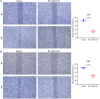
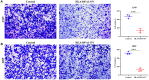
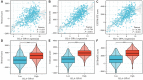
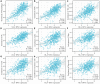
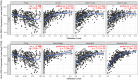
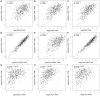
Results: HLA-DPA1 expression is downregulated in LUAD tissues and is associated with gender, race, age, smoking history, clinical stage, histological type, lymph node metastasis, and prognosis of patients with LUAD. HLA-DPA1 is involved in immune responses, leukocyte cell-cell adhesion, and antigen processing and presentation. Overexpression of HLA-DPA1 inhibits cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion while promoting cell sensitivity to cisplatin in A549 and A549/DDP cells. Additionally, overexpression of HLA-DPA1 correlates with tumor purity, stromal, immune, and ESTIMATE scores, the abundance of immune cells (B cells, CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils), and immune cell markers (programmed cell death 1, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4, and cluster of differentiation 8A).
Conclusions: Decreased HLA-DPA1 expression is associated with poor prognosis and immune infiltration in LUAD while HLA-DPA1 overexpression inhibits cancer cell proliferation and progression. Therefore, HLA-DPA1 shows potential as a prognostic biomarker and a therapeutic target for LUAD.
Keywords: The Cancer Genome Atlas; human leukocyte antigen-DP alpha 1; immune infiltration; lung adenocarcinoma; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Overexpression of MTFR1 promotes cancer progression and drug-resistance on cisplatin and is related to the immune microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jan 2;16(1):66-88. doi: 10.18632/aging.205338. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38170222 Free PMC article.
-
TOX correlates with prognosis, immune infiltration, and T cells exhaustion in lung adenocarcinoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Sep;9(18):6694-6709. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3324. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32700817 Free PMC article.
-
ncRNAs-mediated TIMELESS overexpression in lung adenocarcinoma correlates with reduced tumor immune cell infiltration and poor prognosis.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 23;19(1):e0296829. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296829. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38261568 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of GLUT1 on the Survival Rate and Immune Cell Infiltration of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta and Bioinformatics Analysis.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(2):223-238. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210708115406. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34238200 Review.
-
Lysosomal transmembrane protein 5: Impact on immune cell function and implications for immune-related deficiencies.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 22;10(17):e36705. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36705. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281638 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The potential applications of peptide-loading complex in cancer treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 3;16:1526137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1526137. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40098955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with a Diagnosis of COPD: Is This a Hidden Prognosticator for Survival and a Risk Factor for Immune-Related Adverse Events?Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 22;16(7):1251. doi: 10.3390/cancers16071251. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38610929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ding Y, Zhang L, Guo L, Wu C, Zhou J, Zhou Y, Ma J, Li X, Ji P, Wang M, Zhu W, Shi C, Li S, et al.. Comparative study on the mutational profile of adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma predominant histologic subtypes in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients. Thorac Cancer. 2020; 11:103–12. 10.1111/1759-7714.13208 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

